COVID-19 mortality among people living with HIV/AIDS in Brazil: a multilevel analysis
- PMID: 41137093
- PMCID: PMC12551308
- DOI: 10.1186/s12981-025-00759-z
COVID-19 mortality among people living with HIV/AIDS in Brazil: a multilevel analysis
Abstract
Background: The simultaneous COVID-19 and HIV/AIDS pandemics have created unprecedented challenges, disrupting healthcare for people living with HIV/AIDS (PLWHA) and introducing an additional lethal threat. However, the impact of COVID-19 among PLWHA in Brazil remains unclear. We aimed to investigate the association between HIV infection and COVID-19 mortality in the Brazilian population.
Methods: A multilevel study was conducted using data from the Brazilian Mortality Information System. We examined COVID-19 mortality among individuals with and without mention of HIV on their death certificates from 2020 to 2022. Mixed generalized linear regression models were used, considering the COVID-19 dominant Variant of Concern (VOC) and the vaccine rollout period, adjusted for age group and sex, interaction between HIV and age group, and random effects for federative units.
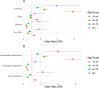
Results: A total of 4,773,337 deaths were analyzed, including 39,011 among PLWHA. Younger (18-39) and older (80+) PLWHA had higher odds of COVID-19 death, particularly during Delta and Omicron periods. Mortality odds among PLWHA were lower during the vaccination expansion phase but increased during the consolidated phase. Regional disparities were observed, with higher mortality odds in Northern and Northeastern Brazil.
Conclusions: HIV infection was associated with higher COVID-19 mortality in Brazil, particularly in specific age groups and regions. Older adults with HIV had an elevated risk of COVID-19 death across all periods. The vaccine rollout reduced COVID-19 mortality among PLWHA, but the results did not hold over time, as evidenced by the increased odds of death in all age groups following vaccination coverage consolidation in the population.
Keywords: COVID-19; Effect modifier; Epidemiologic; HIV; Mortality; Multilevel analysis; SARS-CoV-2.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of the Sergio Arouca National School of Public Health, Oswaldo Cruz Foundation (ENSP/Fiocruz; number 7.210.374). Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- UNAIDS. Brazil | UNAIDS [Internet]. 2024. https://www.unaids.org/en/regionscountries/countries/brazil. Accessed 9 Mar 2025
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

