Unveiling health inequalities and frontier gaps in elderly-onset rheumatoid arthritis: evolving impact of smoking and future challenges
- PMID: 41140659
- PMCID: PMC12546154
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1664232
Unveiling health inequalities and frontier gaps in elderly-onset rheumatoid arthritis: evolving impact of smoking and future challenges
Abstract
Background: Elderly-onset rheumatoid arthritis (EORA) poses a growing public health burden worldwide. Significant health inequalities and frontier gaps persist across countries, while the impact of smoking on EORA has evolved over time.
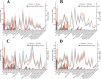
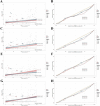
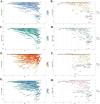
Methods: Using data from the 2021 Global Burden of Disease data, we assessed the incidence, prevalence, mortality, and disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) of EORA and analyzed trends by calculating the estimated annual percentage changes. We explored associations with the sociodemographic index (SDI), evaluated frontier gaps, quantified health inequalities, examined the impact of smoking, and predicted trends to 2050 using Bayesian age-period-cohort (BAPC) models.
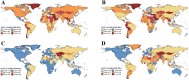
Results: In 2021, global EORA case numbers were as follows: incidence: 0.33 million (95% uncertainty interval [UI]: 0.22, 0.47), prevalence: 7.92 million (95% UI: 6.90, 9.10), mortality: 33.20 thousand (95% UI: 26.86, 38.57), and DALYs: 1.55 million (95% UI: 1.23, 1.93). The disease burden was higher in females than in males, with high SDI-regions such as Australia experiencing the highest burden. Trends varied across different regions and countries; India and China had the highest case numbers, whereas Guam and Singapore showed significant improvements in mortality rates. Cross-national inequality analysis revealed significant disparities in disease burden. Frontier analysis identified considerable potential for improvement in disease burden in several countries and regions. The impact of smoking on EORA has declined, but BAPC model projections indicate that the burden will continue to rise until 2050.
Conclusion: Elderly-onset rheumatoid arthritis has become a significant public health concern. Addressing socio-economic inequalities, enhancing monitoring systems, and implementing targeted prevention and treatment strategies are crucial for alleviating the global EORA burden.
Keywords: disability-adjusted life years; global burden of disease study; incidence; mortality; prevalence; rheumatoid arthritis.
Copyright © 2025 Gao, Jia, Yu, Han, Wang, Zheng, Yang and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Russell M, Gibson M, Zuckerman B, Kumar K, Dubey S, Adas M, et al. Factors associated with biological and targeted synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drug initiation for rheumatoid arthritis in underserved patient groups in England and Wales, UK: a national cohort study. Lancet Rheumatol. (2025) 7:e44–54. 10.1016/S2665-9913(24)00221-2 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

