Randomized Trial of Dapagliflozin in Patients With Nondiabetic Stage 4 CKD
- PMID: 41141510
- PMCID: PMC12545560
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ekir.2025.07.020
Randomized Trial of Dapagliflozin in Patients With Nondiabetic Stage 4 CKD
Abstract
Introduction: Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors are nephroprotective in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) and mild-to-moderate renal insufficiency.
Methods: This prospective, randomized, cross-over, placebo-controlled, double-blind study compared the effects of 6-week dapagliflozin (10 mg/d) with placebo treatment in 31 consenting nondiabetic Caucasian adults with stage 4 CKD and proteinuria > 0.5 g/24 h. Participants were identified at the Nephrology Unit of Papa Giovanni XXIII Hospital and treated at Mario Negri Institute (Bergamo, Italy) between December 2021 and December 2023. Normalized glomerular filtration rate (GFR) (using iohexol plasma clearance) and 24-hour proteinuria (median of 3 urinary measurements) were co-primary outcomes. Analyses were by modified intention-to-treat.
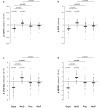
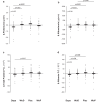
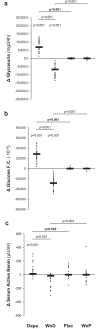
Results: At 6 weeks, dapagliflozin significantly decreased GFR by 1.88 ± 5.00 ml/min per 1.73 m2 (P = 0.022) and proteinuria by 0.50 (-0.10 to 0.80) g/24 h (P = 0.026) versus placebo. The dapagliflozin-induced GFR (P < 0.001) and proteinuria (P = 0.003) reduction was already significant at 1 week. At 6 weeks, dapagliflozin reduced absolute GFR (P = 0.026), the CKD-Epidemiology Collaboration (CKD-Epi) equation-based estimated GFR (eGFR) (P = 0.003), the Modification of Diet in Renal Disease (MDRD) equation-based eGFR (P = 0.002), 24-hour albuminuria (P = 0.001), total protein (P = 0.057) and albumin (P = 0.009) fractional clearances, and fasting blood glucose (P < 0.001); and increased serum albumin (P = 0.001), renin activity (P = 0.020), glucosuria (P < 0.001), and glucose fractional clearance (P < 0.001) versus placebo. All changes reversed completely after treatment withdrawal. GFR changes correlated inversely with changes in renal plasma flow (RPF) (P = 0.010) and positively with changes in postglomerular resistance (P < 0.001) but did not correlate with changes in preglomerular resistance. There were no serious adverse events.
Conclusion: Dapagliflozin safely ameliorates (compensatory) glomerular hyperfiltration and proteinuria and is glycosuric in nondiabetic patients with preterminal CKD. GFR reduction is likely because of postglomerular vasodilation rather than preglomerular vasoconstriction.
Keywords: CKD; GFR; SGLT2 inhibitors; dapagliflozin; hyperfiltration; proteinuria.
© 2025 International Society of Nephrology. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures



References
-
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD Work Group KDIGO 2012 clinical practice guideline for the evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int Suppl. 2012;2013(1):3.
-
- American Society of Nephrology The hidden epidemic: worldwide, over 850 million people suffer from kidney diseases. https://www.asn-online.org/news/2018/0626-Joint_Hidden_Epidem.pdf Accessed February 1, 2025.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

