Global Hip Offset is an Important Factor in the Success of Abductor Mechanism Insufficiency Repair After Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Case Series
- PMID: 41141558
- PMCID: PMC12549797
- DOI: 10.1016/j.artd.2025.101861
Global Hip Offset is an Important Factor in the Success of Abductor Mechanism Insufficiency Repair After Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Case Series
Abstract
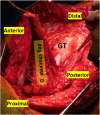
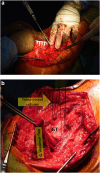
Background: Hip abductor mechanism deficiency due to abductor tendon degeneration, tear, or intraoperative damage during total hip arthroplasty (THA) may cause severe walking disability. For severe abductor weakness in native hip joints, Whiteside muscle transfer is a good solution. However, the literature on the results of abductor mechanism reconstruction (AMR) after THA remains limited. Our study aimed to assess the outcome of AMR in patients with THA suffering from Milwaukee III and IV hip abductor deficiency.
Methods: We conducted a single-center retrospective cohort study of THA with hip abductor mechanism deficiency treated surgically with AMR. Data were collected between January 2011 and December 2019 and included the following parameters: patient's data, subjective level of pain, Harris Hip Score (HHS), gait pattern, extent of hip abductor tear, and offset measurements.
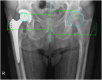
Results: The cohort included 16 THAs with AMR in 16 patients. The whole group median HHS improved from 37.1 interquartile range (IQR) (31.0-38.7) to 73.9 IQR (63.5-83.7) (P < .001). In a subgroup of 9 hips, the global offset was preserved after THA while it was reduced in remaining 7 hips. All patients with preserved global offset had significantly better clinical outcome compared to the group with reduced global offset (median HHS improvement was 48 IQR [46-53] compared to 22 IQR [18-25], P = .001).
Conclusions: Our study showed favorable outcome of the AMR for chronic, Milwaukee III and IV hip abductor deficiency after THA. It is the first study to show that restoration of global offset after THA is of utmost importance to avoid chronic abductor mechanism deficiency.
Keywords: Abductor reconstruction; Abductor repair; Gluteus transfer; Offset; Whiteside procedure.
© 2025 The Authors.
Figures






References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

