Mathematical Modeling of H1-Antihistamines: A QSPR Approach Using Topological Indices
- PMID: 41141767
- PMCID: PMC12547784
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.5c07577
Mathematical Modeling of H1-Antihistamines: A QSPR Approach Using Topological Indices
Abstract
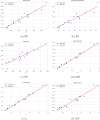
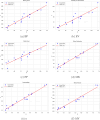
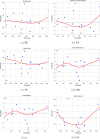
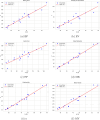
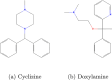
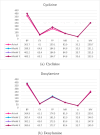
Allergic diseases represent a significant global health burden, requiring effective and safe therapeutic agents for long-term management. H1-antihistamines are among the most widely prescribed and over-the-counter drugs for treating allergic conditions, yet their variable physicochemical and pharmacokinetic properties present challenges in optimizing drug selection, safety, and efficacy. A systematic exploration of their structure-property relationships is, therefore, essential for guiding rational drug design. In this study, the Quantitative Structure-Property Relationship (QSPR) of a selection of H1-antihistamines, including both conventional and second-generation compounds, is investigated by using degree-based topological indices and linear regression models. The computed indices are systematically correlated to key physicochemical properties, revealing strong and statistically significant relationships. These findings provide deeper insights into the molecular factors influencing drug behavior and highlight the predictive utility of topological descriptors. Overall, the developed QSPR models not only enhance the understanding of H1-antihistamines but also establish a framework that can accelerate the identification and optimization of next-generation agents with improved pharmacological profiles.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Figures


References
-
- Tripathi, K. Essentials of Medical Pharmacology, 8th ed.; Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers: New Delhi, India, 2018.
-
- Schaefer, T. S. ; Patel, P. ; Zito, P. M. . Antiemetic histamine H1 receptor blockers. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, 2024. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK533003/. - PubMed
-
- Farzam, K. ; Sabir, S. ; O’Rourke, M. C. . Antihistamines. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, 2025. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK538188/. - PubMed
-
- Pirahanchi, Y. ; Sharma, S. . Physiology, bradykinin. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing, 2023. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
