Human-in-the-Loop Artificial Intelligence System for Systematic Literature Review: Methods and Validations for the AutoLit Review Software
- PMID: 41143167
- PMCID: PMC12552804
- DOI: 10.1002/cesm.70059
Human-in-the-Loop Artificial Intelligence System for Systematic Literature Review: Methods and Validations for the AutoLit Review Software
Abstract
Introduction: While artificial intelligence (AI) tools have been utilized for individual stages within the systematic literature review (SLR) process, no tool has previously been shown to support each critical SLR step. In addition, the need for expert oversight has been recognized to ensure the quality of SLR findings. Here, we describe a complete methodology for utilizing our AI SLR tool with human-in-the-loop curation workflows, as well as AI validations, time savings, and approaches to ensure compliance with best review practices.
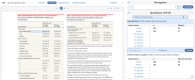
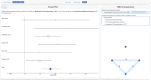
Methods: SLRs require completing Search, Screening, and Extraction from relevant studies, with meta-analysis and critical appraisal as relevant. We present a full methodological framework for completing SLRs utilizing our AutoLit software (Nested Knowledge). This system integrates AI models into the central steps in SLR: Search strategy generation, Dual Screening of Titles/Abstracts and Full Texts, and Extraction of qualitative and quantitative evidence. The system also offers manual Critical Appraisal and Insight drafting and fully-automated Network Meta-analysis. Validations comparing AI performance to experts are reported, and where relevant, time savings and 'rapid review' alternatives to the SLR workflow.
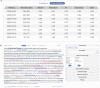
Results: Search strategy generation with the Smart Search AI can turn a Research Question into full Boolean strings with 76.8% and 79.6% Recall in two validation sets. Supervised machine learning tools can achieve 82-97% Recall in reviewer-level Screening. Population, Interventions/Comparators, and Outcomes (PICOs) extraction achieved F1 of 0.74; accuracy for study type, location, and size were 74%, 78%, and 91%, respectively. Time savings of 50% in Abstract Screening and 70-80% in qualitative extraction were reported. Extraction of user-specified qualitative and quantitative tags and data elements remains exploratory and requires human curation for SLRs.
Conclusion: AI systems can support high-quality, human-in-the-loop execution of key SLR stages. Transparency, replicability, and expert oversight are central to the use of AI SLR tools.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; evidence synthesis; human‐in‐the‐loop; meta‐analysis; systematic literature review.
© 2025 The Author(s). Cochrane Evidence Synthesis and Methods published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of The Cochrane Collaboration.
Figures


References
-
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE). Use of AI in Evidence Generation– NICE Position Statement. NICE. Published October 2023, accessed May 29, 2025, https://www.nice.org.uk/about/what-we-do/our-research-work/use-of-ai-in-....
-
- Rycroft C. E., Fernandez M., and Copley‐Merriman C., “Systematic Literature Reviews at the Heart of Health Technology Assessment: A Comparison Across Markets,” Value in Health 16, no. 7 (2013): A481, 10.1016/j.jval.2013.08.1236. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
