Oral anticoagulant reversal and mortality in trauma patients: a multicentre propensity score-matched cohort study
- PMID: 41146925
- PMCID: PMC12554126
- DOI: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2025.103577
Oral anticoagulant reversal and mortality in trauma patients: a multicentre propensity score-matched cohort study
Abstract
Background: Oral anticoagulant (OAC) therapy increases bleeding risk but its impact on trauma outcomes and the benefit of reversal remains uncertain. This study aimed to evaluate 1/the effect of preinjury OAC therapy on trauma mortality and 2/the protective role of OAC reversal and its associated thrombotic risk.
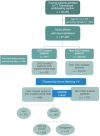
Methods: We conducted an observational study using a prospective multicenter trauma registry between January 2012 and December 2023. OAC-treated patients were matched with non-OAC-treated patients using a propensity score. Univariable and multivariable logistic regressions assessed associations between OAC therapy and day 1 and day 7 mortality. The effect of guideline-concordant OAC reversal was evaluated. Thrombotic complications were recorded.
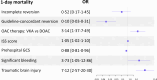
Findings: Of the 27,426 trauma patients, 3% were OAC-treated. They were older, had more comorbidities, and experienced higher mortality. After matching (n = 2196), OAC therapy remained independently associated with increased mortality (day 1: OR 2·21, 95% CI [1·41-3·43]; day 7: OR 2·06, [1·41-3·00]), with greater risk from vitamin K antagonists (VKA) than direct oral anticoagulants (DOAC). Guideline-concordant OAC reversal, achieved only in 21% of cases, independently reduced mortality at day 1 (OR 0·10, 95% CI [0·03-0·31], p < 0·01) and day 7 (OR 0·51, 95% CI [0·22-0·97], p < 0·01). No significant association was found between reversal and thrombotic complications.
Interpretation: Preinjury OAC therapy substantially increased trauma mortality, particularly with VKA. Guideline-concordant reversal was associated with reduced mortality in both VKA- and DOAC-treated patients without excess thrombotic risk but remains underused. These findings emphasise the urgent need for systematic implementation of reversal strategies in OAC-treated trauma patients.
Funding: The Traumabase registry is funded by several Regional Health Agencies (Agences Régionales de Santé, ARS): ARS Île-de-France, ARS Occitanie, ARS Grand Est, ARS Hauts-de-France, and ARS Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes. The registry is also funded by the French Road Safety Observatory-Road Safety Delegation Service (Observatoire National Interministériel de la Sécurité Routière-Délégation à la Sécurité Routière).
Keywords: Bleeding; Mortality; Oral anticoagulant; Reversal; Thrombosis; Trauma.
© 2025 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Elodie Lang, Marion Gautier, Fanny Vardon, Vincent Legros, Jean-Luc Hanouz, Florent Hericher, Olivier Duranteau, Pierre-Antoine Allain, Benjamin Popoff, Thomas Botrel, and Jean Pasqueron declare no competing interests. Anne Godier reports personal fees from Aguettant, Alexion, Bayer Healthcare, BMS-Pfizer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Sanofi, CSL Behring, LFB, Octapharma, Stago, and Viatris. Delphine Garrigue Huet reports personal fees from LFB, Octapharma, Chugai, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bayer, and AstraZeneca. Gérard Audibert reports personal fees from LFB and Octapharma. Gary Duclos reports lecture fees from AOP Health. Paer-Sélim Abback reports personal fees from LFB. Samy Figueiredo reports personal fees from Edwards Lifesciences and Octapharma.
Figures



References
-
- Floccard B., Rugeri L., Faure A., et al. Early coagulopathy in trauma patients: an on-scene and hospital admission study. Injury. 2012;43:26–32. - PubMed
-
- Deras P., Villiet M., Manzanera J., et al. Early coagulopathy at hospital admission predicts initial or delayed fibrinogen deficit in severe trauma patients. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2014;77:433–440. - PubMed
-
- Kietaibl S., Ahmed A., Afshari A., et al. Management of severe peri-operative bleeding: guidelines from the European Society of Anaesthesiology and Intensive Care: second update 2022. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2023;40:226–304. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

