Apparent diffusion coefficient as a quantitative biomarker for prostate cancer treatment response on a 1.5 Tesla magnetic resonance-linear accelerator: Impact of image registration and acquisition type
- PMID: 41146990
- PMCID: PMC12554063
- DOI: 10.1016/j.phro.2025.100851
Apparent diffusion coefficient as a quantitative biomarker for prostate cancer treatment response on a 1.5 Tesla magnetic resonance-linear accelerator: Impact of image registration and acquisition type
Abstract
Background and purpose: Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (DW-MRI) is a quantitative biomarker for cancer detection and treatment monitoring. On magnetic resonance-linear accelerator (MR-Linac) systems, diffusion-weighted echo planar imaging (DW-EPI) suffers from geometric distortion, reducing the repeatability of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) measurements. This study evaluated the effect of low-distortion split acquisition of fast spin-echo signal (SPLICE) sequences, and of image registration on the repeatability coefficient (RC) of ADC.
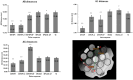
Materials and methods: ADC bias, repeatability, signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and geometric fidelity were measured in a diffusion phantom using three DW-EPI and two DW-SPLICE protocols. ADC short-term and long-term RCs were measured in healthy volunteers. In patients, the registration of DW-EPI to unweighted images (b0) was tested for its effect on RC in gross tumour volume (GTV) and non-tumour prostate (NT-P), and for its ability to detect significant ADC changes.
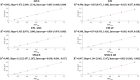
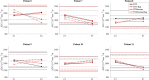
Results: Phantom experiments showed strong linear correlation with ground-truth ADC (R2 > 0.99). Among EPI protocols, DW-EPI-AP offered the best balance of high SNR and low RC, while Z-direction encoded DW-EPI was the most variable. Both DW-SPLICE variants exhibited reduced distortion compared with EPI but poorer repeatability. In volunteers, long-term RCs (8.0-33.7 %) varied more than short-term RCs (8.9-15.4 %). In patients, registration improved RCs (GTV: 28.0 → 25.1 %; NT-P: 19.6 → 12.6 %) and improved detection of significant ADC change in patients (GTV: 0/6 → 1/6; NT-P: 2/6 → 5/6).
Conclusion: RC and accuracy of DW-EPI agrees with published literature and improves after registration. DW-SPLICE shows lower geometric distortion but would require further optimization and validation to improve repeatability.
Keywords: Apparent diffusion coefficient; Diffusion weighted echo planar imaging; Geometric distortion correction; MR-Linac; Repeatability coefficient.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: PPN, JC, MN, BL, SC, ACT, PJvH, UO and AW declare the following conflict: The Institute of Cancer Research (ICR), the Royal Marsden Hospital (RMH) and the Netherlands Cancer Institute (NKI) are members of the MR-Linac Consortium with industrial partners Elekta and Philips. ICR and RMH receive research support from Elekta and Philips. ACT receives research funding from Elekta, Varian and Accuray, honoraria/travel assistance from Elekta, Accuray, Bayer and Janssen. ACT is chair of the MR linac consortium steering committee.
Figures




References
-
- Verma S., Rajesh A., Morales H., Lemen L., Bills G., Delworth M., et al. Assessment of aggressiveness of prostate cancer: correlation of apparent diffusion coefficient with histologic grade after radical prostatectomy. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011;196(2):374–381. doi: 10.2214/AJR.10.4441. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

