Neurotoxic Effects of Bisphenol (BPA): Mini-Reviews
- PMID: 41150587
- PMCID: PMC12567624
- DOI: 10.3390/toxics13100888
Neurotoxic Effects of Bisphenol (BPA): Mini-Reviews
Abstract
Introduction: Bisphenol A (BPA) is a synthetic compound widely used in plastics and epoxy resins, and human exposure is virtually unavoidable. Numerous studies indicate that even doses below current regulatory limits may elicit neurotoxic effects, impairing learning, memory, and synaptic plasticity.
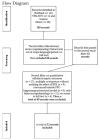
Methodology: This mini-review. Searches were conducted in PubMed, the Virtual Health Library (VHL/BVS), and ScienceDirect, using MeSH descriptors related to "Bisphenol A," "Neurotoxicity Syndromes," "Central Nervous System," and "Prefrontal Cortex," combined with Boolean operators. We included studies published between 2007 and 2025, available in English, Portuguese, or Spanish, and focused on the neurotoxic effects of BPA. After screening and application of the eligibility criteria, twelve articles were selected.
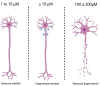
Results: The analyzed studies show that BPA exposure, even at low concentrations, compromises neuronal survival, dendritic density, and synaptic plasticity. In animal models, cognitive deficits were observed in memory and learning tasks, associated with increased oxidative stress and alterations in molecular pathways such as AMPK, HO-1, and nNOS/Keap1/Nrf2. In cell cultures, BPA induced apoptosis, autophagy dysfunction, cytoskeletal reorganization, and loss of synaptic proteins. The effects were dose-dependent and, in some cases, sex-dependent.
Conclusions: BPA exhibits significant neurotoxic potential, affecting both the development and function of the central nervous system. These findings underscore the need to revise current safety limits and reinforce the importance of public policies regulating BPA use, as well as encouraging the search for safer alternatives.
Keywords: bisphenol A; hippocampus; neurotoxicity; prefrontal cortex.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest declared by the authors.
Figures
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

