Estimation of protein content in wheat samples using NIR hyperspectral imaging and 1D-CNN
- PMID: 41152319
- PMCID: PMC12569077
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-15408-8
Estimation of protein content in wheat samples using NIR hyperspectral imaging and 1D-CNN
Abstract
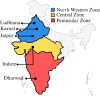
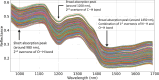
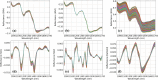
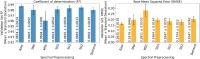
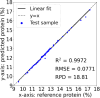
Wheat protein content is a major determinant of its usage and value. Current methods require wet labs that may be difficult to access and are not real-time. To overcome this, Hyperspectral imaging (HSI) has been reported for estimating the protein content of wheat seeds with the advantage that it is real-time, does not require wet labs, and has high accuracy. However, these models have been developed and validated for a small range of protein content, and without considering cultivation regions. This paper reports the extension of the use of HSI for protein estimation for a wider range of protein content and for wheat cultivated in different regions. Hyperspectral images of 621 wheat samples from five regions in India were acquired in the 900-1700 nm wavelength range. The reference protein content of each sample was determined using the Kjeldahl method, with values ranging from 9.5 to 17.25%. Mean spectra were extracted from the hyperspectral images to develop deep learning and conventional machine learning methods, which were validated through 5-fold cross-validation. The experiments showed that the one-dimensional convolutional neural networks (1D-CNN) performed the best, with the coefficient of determination (R²) of 0.9972, root mean square error (RMSE) of 0.0771, and the ratio of performance to deviation (RPD) of 18.81 for the prediction set. This shows that a 1D-CNN model trained using mean spectra can accurately estimate the wheat protein content. This has the advantage of not requiring a wet lab, and being potentially real-time, which could benefit the farmers, traders, and food industry.
Keywords: Convolutional neural network; Near-infrared hyperspectral imaging; Non-destructive quality evaluation; Spectral data extraction; Wheat protein.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Shuqin, Y., Dongjian, H. & Jifeng, N. Predicting wheat kernels ’ protein content by near infrared hyperspectral imaging. International Journal of Agricultural and Biological Engineering.9, 163–170 (2016).
-
- Shi, T. et al. Using VIS-NIR hyperspectral imaging and deep learning for non-destructive high-throughput quantification and visualization of nutrients in wheat grains. Food Chem.461, 140651 (2024). - PubMed
-
- Wang, B. et al. The applications of hyperspectral imaging technology for agricultural products quality analysis: A review. Food Rev. Int.39, 1043–1062 (2023).
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

