The Involvement of Endothelin-1 in Sepsis and Organ Dysfunction-A Novel Biomarker in Patient Assessment
- PMID: 41153763
- PMCID: PMC12561028
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines13102480
The Involvement of Endothelin-1 in Sepsis and Organ Dysfunction-A Novel Biomarker in Patient Assessment
Abstract
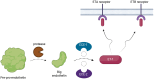
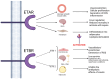
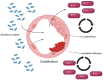
Sepsis represents a life-threatening organ dysfunction caused by a dysregulated host response to infection, and is considered a medical emergency. Therefore, quick diagnosis and treatment are required in order to improve survivability. Currently, patient evaluation in sepsis is based on the Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score to determine the severity of the disease; however, novel biomarkers are also actively researched with the aim to develop quicker diagnostic tools and better therapy. Endothelin-1 is one of the most potent vasoconstrictors found in the human body and is involved in the pathophysiology of both sepsis and other conditions involving organs that make up the SOFA score. In this narrative review, we aimed to gather information of this peptide's multiple effects and to help determine whether or not it could prove a valuable biomarker in the evaluation of patients with multi-organ dysfunction in sepsis.
Keywords: biomarker; cardiovascular dysfunction; endothelin receptor; endothelin-1; liver dysfunction; multi-organ dysfunction; neurological diseases; pulmonary dysfunction; renal dysfunction; sepsis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Prepeliuc C.S., Miftode I.L., Pasare M.A., Miftode R.S., Stamateanu L.O., Costache I.I., Costache A.D., Miftode E. The search for novel biomarkers in sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy—A new challenge to overcome. Rom. J. Pharm. Pract. 2022;15:94–99. doi: 10.37897/RJPhP.2022.3.3. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources