A Novel tRF-Lys-TTT-012 in Qingyu Pigs Mediates the Conversion of Muscle Fibers from Fast-Twitch to Slow-Twitch Type
- PMID: 41153971
- PMCID: PMC12561626
- DOI: 10.3390/ani15203044
A Novel tRF-Lys-TTT-012 in Qingyu Pigs Mediates the Conversion of Muscle Fibers from Fast-Twitch to Slow-Twitch Type
Abstract
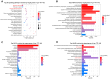
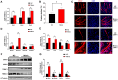
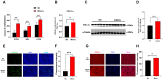
Skeletal muscle, the largest organ within the animal body, consists of multiple muscle fiber types. The distribution of these fiber types significantly impacts both athletic performance and the quality of meat. Growing evidence has demonstrated that transfer RNA (tRNA)-derived small RNAs (tsRNAs) are not merely byproducts of tRNA metabolism but also participate in multiple cellular metabolic processes. However, the role of tsRNAs in skeletal muscle fiber type transition remains elusive. In this study, a total of 403 differentially expressed tsRNAs were identified through small RNA sequencing in psoas major muscle (PM) and latissimus dorsi muscle (LD), among which 220 tsRNAs including tRF-Lys-TTT-012 were upregulated in psoas major muscle. Functional studies in C2C12 and PK15 cells demonstrated that it inhibited the proliferative capacity of C2C12 cells while promoting myogenic differentiation, increased the proportion of slow muscle fibers after differentiation, and drove muscle fiber type transition toward slow fibers. Additionally, tRF-Lys-TTT-012 enhanced mitochondrial number and function, potentially linking to the promotion of slow fiber characteristics. Collectively, tRF-Lys-TTT-012 may serve as a promising marker for slow muscle fibers and uncover a novel potential target for skeletal muscle fiber type transition toward the slow fiber phenotype.
Keywords: mitochondria; skeletal muscle fiber type; tsRNA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures





References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

