Neurofibromin Encoded by the Neurofibromatosis Type 1 (NF1) Gene Promotes the Membrane Translocation of SPRED2, Thereby Inhibiting the ERK Pathway in Breast Cancer Cells
- PMID: 41155378
- PMCID: PMC12563662
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms262010072
Neurofibromin Encoded by the Neurofibromatosis Type 1 (NF1) Gene Promotes the Membrane Translocation of SPRED2, Thereby Inhibiting the ERK Pathway in Breast Cancer Cells
Abstract
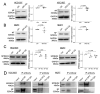
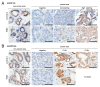
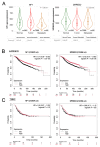
Neurofibromin (NF) inhibits the RAS/RAF/ERK pathway through its interaction with SPRED1 (Sprouty-related EVH1 domain-containing protein 1). Here, we investigated the functional relationship between NF and SPRED2 in breast cancer (BC). Human BC cell lines were transfected to downregulate or overexpress NF and SPRED2 and subsequently subjected to functional assays. Protein and mRNA levels were analyzed by Western blotting and RT-qPCR, respectively. Protein-protein interactions were examined by immunoprecipitation. Database analyses and immunohistochemistry (IHC) of BC tissues were performed to validate the in vitro findings. Downregulating NF or SPRED2 expression in BC cells enhanced cell proliferation, migration and invasion accompanied by RAF/ERK activation, whereas overexpression produced opposite effects. NF formed a protein complex with SPRED2 and facilitated its translocation to the plasma membrane. By IHC, SPRED2 membrane localization was absent in NF-negative luminal A and triple-negative BC (TNBC) but present in a subset of luminal A BC. By database analyses, both NF1 and SPRED2 mRNA levels were reduced in BC tissues, and luminal A BC patients with high expression of both NF1 and SPRED2 mRNA exhibited improved relapse-free survival. These results suggest a critical role for the NF-SPRED2 axis in BC progression and highlight it as a potential therapeutic target.
Keywords: RAS/RAF/ERK; SPRED2; breast cancer; neurofibromatosis type 1; neurofibromin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures





References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

