Molecular Biomarkers and Therapeutic Approach of Patients with Diabetes and Obstructive Sleep Apnea
- PMID: 41155523
- PMCID: PMC12564514
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms262010234
Molecular Biomarkers and Therapeutic Approach of Patients with Diabetes and Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Abstract
The bidirectional relationship between obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) represents a critical intersection in metabolic medicine. Therefore, the present review examines the most recent data regarding molecular mechanisms linking OSA and T2DM, analyzing key biomarkers including hypoxia-inducible factors (HIF 1α), inflammatory mediators, adipokines, microRNAs, hormones, and neuropeptides that serve as both diagnostic indicators and potential therapeutic targets. Key molecular findings from the scientific literature report elevated HIF-1α promoting insulin resistance, decreased SIRT1 levels, dysregulated microRNA-181a and microRNA-199a, increased inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6, CRP), and altered adipokine profiles with reduced adiponectin and elevated leptin and resistin. Current clinical evidence reveals significant therapeutic potential for modern antidiabetic medications in the management of OSA. GLP-1 receptor agonists, particularly tirzepatide, received FDA approval as the first medication for moderate-to-severe OSA in obese adults, showing a 55-63% AHI reduction. SGLT2 inhibitors also demonstrate promising results through weight loss and cardiovascular protection mechanisms. This integrated approach represents the evolution toward comprehensive OSA management beyond traditional mechanical ventilation strategies. Future research should focus on developing personalized treatment algorithms based on individual molecular biomarker profiles, investigating combination therapies, and exploring novel targets, including chronotherapy agents.
Keywords: GLP-1RAs; SGLT2 inhibitors; clinical evidence; molecular markers; molecular mechanisms; obstructive sleep apnea; tirzepatide; type 2 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

 = Activation.
= Activation.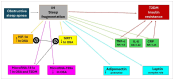
 = Activation;
= Activation;  = Inhibition.
= Inhibition.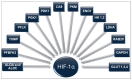
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

