Lactulose, Rifaximin, and Survival in Hepatic Encephalopathy: A Cohort Study of 120 Patients
- PMID: 41156201
- PMCID: PMC12565197
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm14207331
Lactulose, Rifaximin, and Survival in Hepatic Encephalopathy: A Cohort Study of 120 Patients
Abstract
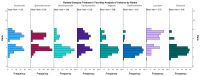
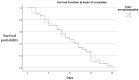
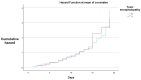
Background: Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) is a severe neuropsychiatric complication of advanced liver disease, driven primarily by ammonia accumulation due to impaired hepatic detoxification and portosystemic shunting. Lactulose is a cornerstone therapy, while rifaximin serves as an effective adjunct for reducing recurrence and hospitalizations. Methods: We conducted a retrospective cohort study at Constanța Emergency County Hospital from January 2022 to March 2025, including 120 adult patients diagnosed with HE. Inclusion criteria were confirmed diagnosis of cirrhosis with clinical and/or biochemical evidence of HE. Patients with other primary neurological disorders or incomplete medical records were excluded. Data on demographics, comorbidities, laboratory results, and medications were collected. Statistical analyses were performed employing descriptive statistics, Friedman's two-way ANOVA by ranks for medication use, and Cox proportional hazards regression to assess survival associations. Results: The mean age was 61.19 years, with high prevalence of anemia (mean hemoglobin: 9.35 g/dL) and thrombocytopenia (mean: 121.86 × 103/µL). Inflammatory markers were elevated (mean CRP: 36.95 mg/L; ESR: 55.83 mm/h), and INR averaged 1.86. Lactulose was administered to 63.3% of patients, rifaximin to 52.5%, with diuretics, pantoprazole, and albumin being frequently used. Friedman's analysis ranked lactulose highest in usage frequency. Cox regression indicated no significant short-term survival difference associated with toxic encephalopathy or rifaximin use. Conclusion: In this cohort, lactulose remained the primary treatment for HE, often complemented by supportive pharmacotherapy. While rifaximin use was limited, the overall medication patterns reflected standard practice priorities in HE management.
Keywords: cirrhosis; hepatic encephalopathy; lactulose; liver failure; rifaximin; survival analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- BioRender.com Scientific Image and Illustration Software. [(accessed on 11 August 2025)]. Available online: https://www.biorender.com/
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

