Antiviral Activity of Glucosyl Hesperidin Against Feline Calicivirus
- PMID: 41156791
- PMCID: PMC12565987
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms13102332
Antiviral Activity of Glucosyl Hesperidin Against Feline Calicivirus
Abstract
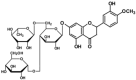
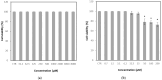
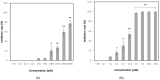
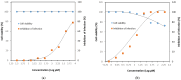
The objective of this study was to evaluate the antiviral activity of glucosyl hesperidin (GH), a water-soluble derivative of hesperidin with known antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, in order to explore its potential applications. Antiviral activity was assessed using feline calicivirus (FCV), a surrogate model for human norovirus, a major foodborne pathogen. Cytotoxicity testing in Crandell-Rees feline kidney (CRFK) cells demonstrated that GH exhibited high biocompatibility, maintaining 100% cell viability at concentrations up to 8000 μM. Antiviral efficacy assays revealed that GH inhibited FCV replication in a concentration-dependent manner across the range of 250~8000 μM, with a half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) of 3281 μM. Complete viral inhibition, however, was not achieved at the maximum concentration tested. In conclusion, GH was shown to inhibit FCV while maintaining low cytotoxicity, indicating its potential as a natural, water-soluble candidate for the suppression of norovirus.
Keywords: antiviral activity; feline calicivirus; flavonoid; glucosyl hesperidin; norovirus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

