Synergistic Effects of High-Modulus Additives on SBS-Modified Asphalt: Microstructural, Rheological Enhancement, and Dosage-Dependent Performance Optimization
- PMID: 41156954
- PMCID: PMC12565973
- DOI: 10.3390/ma18204724
Synergistic Effects of High-Modulus Additives on SBS-Modified Asphalt: Microstructural, Rheological Enhancement, and Dosage-Dependent Performance Optimization
Abstract
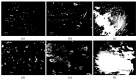
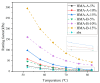
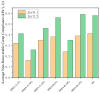
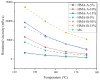
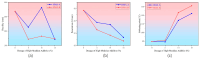
This study systematically investigates the synergistic modification effects of two high-modulus additives on SBS-modified asphalt through microstructural characterization and performance evaluation. Fluorescence microscopic analysis reveals that the additive particles undergo swelling over time and form an interconnected network structure via phase separation dynamics. Rheological tests demonstrate a significant enhancement in high-temperature performance: at the optimal dosage of 10 wt%, the complex modulus increases by approximately 215%, and the rutting factor improves by about 300% compared to the control group. The results from multiple stress creep recovery (MSCR) tests confirm the material's superior elastic recovery capability and reduced non-recoverable creep compliance. However, the incorporation of the additives adversely affects low-temperature ductility. The penetration of (two distinct high-modulus agents, designated as HMA-A and HMA-B) HMA-B decreases by approximately 36.8% more than that of HMA-A, accompanied by significantly lower low-temperature toughness. A dosage of 10% is identified as the critical threshold, which maximizes rutting resistance while minimizing low-temperature performance degradation. Based on these findings, this paper proposes an integrated design paradigm of "microstructure-performance-dosage," recommending HMA-B for high-stress pavement channels and HMA-A for regions with substantial temperature variations.
Keywords: SBS-modified asphalt; composite modification; high-modulus asphalt; high-temperature performance; threshold.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors Qinghua He, Jianqi Huang, Liujun Zhao and Jiabiao Zou were employed by the company Guangzhou Expressway Co., Ltd. Authors Jie Chen and Tong Cui were employed by the company Poly Changda Engineering Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Wang L., Wei J.C., Wu W.J., Zhang X.M., Xu X.Z., Yan X.P. Technical development and long-term performance observations of long-life asphalt pavement: A case study of Shandong Province. J. Road Eng. 2022;2:369–389. doi: 10.1016/j.jreng.2022.11.001. - DOI
-
- Li Q., Yang H., Ni F., Ma X., Luo L. Cause analysis on permanent deformation for asphalt pavements using field cores. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015;100:40–51. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2015.09.012. - DOI
-
- Xing C., Tang S., Chang Z., Han Z., Li H., Zhu B. A comprehensive review on the plant-mixed cold recycling technology of emulsified asphalt: Raw materials and factors affecting performances. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024;439:137344. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2024.137344. - DOI
-
- Tian T., Jiang Y., Yi Y., Nie C. The splitting fatigue properties of ultra-large particle size asphalt mixture under the coupling effect of temperature and load. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2025;319:110990. doi: 10.1016/j.engfracmech.2025.110990. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

