A high-throughput drug screening assay for anti-tau aggregation using split GFP and flow cytometry
- PMID: 41162471
- PMCID: PMC12572213
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-21680-5
A high-throughput drug screening assay for anti-tau aggregation using split GFP and flow cytometry
Abstract
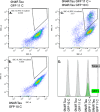
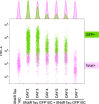
Tau protein aggregation is a hallmark of neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer's disease, making the development of anti-aggregation therapeutics a critical area of research. Progress in drug discovery has been hindered by the lack of efficient screening methods that accurately reflect cellular conditions. We present a high-throughput cell-based assay utilizing split GFP technology to monitor tau aggregation in living cells. Our system employs suspension-adapted HEK293 cells co-transfected with tau proteins fused to complementary GFP fragments, producing fluorescent signals upon tau aggregation. Notably, our system demonstrates tau aggregation without external aggregation inducers, likely due to the enhanced protein expression in suspension-adapted cells. Validation with a known urea-based tau aggregation inhibitor showed dose-dependent reduction in fluorescence, corresponding to decreased tau aggregation. The assay's flow cytometry compatibility enables rapid, quantitative analysis of large sample sets while allowing simultaneous assessment of compound efficacy and cytotoxicity. This method advances tau aggregation monitoring and drug discovery by providing a physiologically relevant platform for identifying novel anti-tau aggregation therapeutics.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

