Validation of Treatment Planning Systems based on Dose Calculation Accuracy for Extended SSD Total Body Irradiation with and without Beam Spoiler
- PMID: 41163771
- PMCID: PMC12560995
- DOI: 10.4103/jmp.jmp_103_25
Validation of Treatment Planning Systems based on Dose Calculation Accuracy for Extended SSD Total Body Irradiation with and without Beam Spoiler
Abstract
Aims: This study aimed to confirm the accuracy of the dose calculation by commercially available treatment planning system (TPS) at the extended SSD = 350 cm with and without beam spoiler configurations.
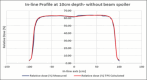
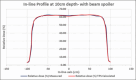
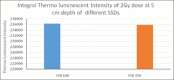
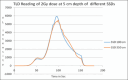
Materials and methods: Two extended SSD plans, one without a beam spoiler and another with a beam spoiler, were created on a virtual phantom in Eclipse TPSs for 6 MV photon beam. Using dosimetry tools, percentage depth doses (PDDs) and in-line profiles of both plans were generated. Beam properties of the TPS calculated PDDs and profiles were compared with manually calculated and measured PDDs and profiles. Reference depth dose was calculated in two different phantoms and measured using an ion chamber and TLDs.
Results: At the extended SSD setup, the TPS calculated and measured PDD with and without beam spoiler were in agreement within 2%. This agreement was observed at the surface and in the buildup region as well. Flatness and symmetry of the profiles with and without beam spoiler were within ± 3%. The TPS calculated dose at a reference depth in a homogeneous and a heterogeneous phantom was agreed with measured dose using an ion-chamber and TLDs.
Conclusion: This study validated the TPS for extended SSD total body irradiation (TBI) dose calculation with and without beam spoiler. Developing computed tomography based field in field plan for homogeneous dose distribution may be feasible. This technique may allow us to treat extended SSD TBI in less time while maintaining dose calculation accuracy.
Keywords: Extended SSD percentage depth dose with beam spoiler; extended source-to-surface distance profile with beam spoiler; extended source-to-surface distance total body irradiation using treatment planning systems.
Copyright: © 2025 Journal of Medical Physics.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures








References
-
- Fog LS, Wirth A, MacManus M, Downes S, Grace M, Moggré A, et al. Total body irradiation in Australia and New Zealand: Results of a practice survey. Phys Eng Sci Med. 2020;43:825–35. - PubMed
-
- Peters M, Taylor B, Turner E. An evidence-based review of total body irradiation. J Med Imaging Radiat Sci. 2015;46:442–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
