Licoricidin Enhances Paclitaxel-induced Apoptosis Through Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Human Cervical Cancer Cells
- PMID: 41167706
- PMCID: PMC12588196
- DOI: 10.21873/invivo.14119
Licoricidin Enhances Paclitaxel-induced Apoptosis Through Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Human Cervical Cancer Cells
Abstract
Background/aim: The adverse side effects associated with chemotherapeutic agents have prompted the exploration of natural compounds as adjuvants to chemotherapy, offering more effective therapeutic alternatives. Licoricidin, a bioactive constituent of licorice, possesses diverse pharmacological properties. However, the antitumor mechanisms underlying the therapeutic effects of Licoricidin combined with paclitaxel in cervical cancer remain unclear and further investigations are warranted.
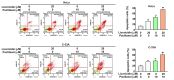
Materials and methods: Cell growth and apoptosis were assessed using the MTT assay and Annexin V/PI staining. Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress was evaluated using the ER-ID assay. The expression of apoptosis- and ER stress-related proteins in response to the combined treatment was analyzed using western blotting.
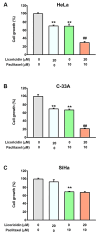
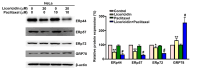
Results: Combined treatment with licoricidin and paclitaxel effectively inhibited cell growth and induced apoptosis in human HeLa and C-33A cells. We further revealed that this combined treatment increased the expression of apoptotic proteins (c-PARP, Bax, and DR5) while decreasing the expression of pro-caspase proteins (pro-caspase-3 and pro-caspase-9) in HeLa cells. In addition, the combined treatment induced ER stress, as evidenced by decreased expression levels of ERp44, ERp57, and ERp72, whereas the expression of GRP78 was increased in HeLa cells.
Conclusion: The combination of licoricidin and paclitaxel induced ER stress-mediated apoptosis and may serve as a potential antitumor therapeutic strategy against human cervical cancer cells.
Keywords: Licoricidin; apoptosis; cervical cancer cells; endoplasmic reticulum; paclitaxel.
Copyright © 2025, International Institute of Anticancer Research (Dr. George J. Delinasios), All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The Authors declare no conflicts of interest to report regarding the present study.
Figures


References
-
- Yao G, Qiu J, Zhu F, Wang X. Survival of patients with cervical cancer treated with definitive radiotherapy or concurrent chemoradiotherapy according to histological subtype: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Med (Lausanne) 2022;9:843262. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.843262. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
