A porcine model of Fanconi anemia
- PMID: 41171815
- PMCID: PMC12578174
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0335854
A porcine model of Fanconi anemia
Abstract
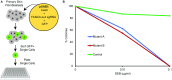
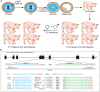
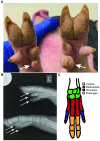
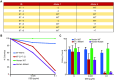
Although small animal models of Fanconi anemia (FA) are useful, they do not faithfully replicate many of the clinical features seen in FA patients. We reasoned that a porcine model of FA with its similar physiology and a relatively long lifespan would produce a phenotype more similar to human FA. Targeting FANCA in domestic swine resulted in skeletal abnormalities and extreme sensitivity to interstrand DNA cross-linking agents. In addition, FANCA disruption followed by mitomycin C treatment resulted in a > 10-fold increase in chromosomal radials, a finding that is considered diagnostic for human FA. Bone marrow derived, hematopoietic progenitor cells from a FANCA null pig showed a 75% reduction in colony forming activity compared to wild type. Evaluation of steady state hematopoiesis in the peripheral blood revealed the gradual development of red cell macrocytosis and a reduction in circulating neutrophils. Targeting of FANCD2 failed to produce any biallelic animals demonstrating the loss of FANCD2 function is embryonic lethal in pigs. These results indicate that a porcine model of FANCA holds promise for the development of strategies to prevent the development of bone marrow failure and malignancies in patients with FA.
Copyright: © 2025 Hergert et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- Eccles LJ, Bell AC, Powell SN. Inhibition of non-homologous end joining in Fanconi Anemia cells results in rescue of survival after interstrand crosslinks but sensitization to replication associated double-strand breaks. DNA Repair (Amst). 2018;64:1–9. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2018.02.003 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

