The intracellular domains of the DSL ligands Serrate and Delta provide different activities
- PMID: 41174722
- PMCID: PMC12577249
- DOI: 10.1186/s12964-025-02472-w
The intracellular domains of the DSL ligands Serrate and Delta provide different activities
Abstract
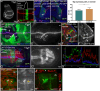
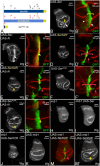
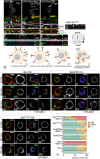
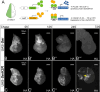
Endocytosis of the ligands is a central requirement for the correct activation of the Notch-signalling pathway. It is initiated by E3-ligase mediated ubiquitylation (ubi) of the intracellular domain (ICD) of the ligands on lysine (K). In Drosophila, two ligands are present, termed Serrate (Ser) and Delta (Dl). They are ubiquitylated by the E3-ligases Mindbomb1 (Mib1) and Neuralized (Neur). Here, we show that the ICDs of Dl and Ser have different activities. We characterised the properties of the Ser-ICD and focused on the meaning of its Ks for ubi and signalling activity. For this purpose, we generated a variant in which all Ks of its ICD are replaced by the structurally similar arginine (R), termed SerK2R. Its analysis revealed that, in contrast to Dl, the Ks are essential for the endocytosis and degradation of Ser by Mib1. Moreover, whereas Dl possesses an ubi- and Mib1-independent signalling activity, Ser-signalling completely depends on Mib1-dependent ubi. We found that a minimum of five conserved Ks in the ICD are required for the Mib1-mediated activation of Ser and that the importance of the individual Ks differs. These core Ks appear to preferentially channel Ser into a rare signalling-relevant endocytosis pathway. Remarkably, the addition of a sixth K largely restores also bulk endocytosis, which is irrelevant for signalling. Thus, at least 6 of the 10 Ks of the ICD are required for the complete activity/behaviour of Ser.
Supplementary Information: The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1186/s12964-025-02472-w.
Keywords: Cis-inhibition; DSL-ligands; Delta; Dl; E3-ligases; Endocytosis; Mib1; Mindbomb1; Notch-pathway; Ser; Serrate; Ubiquitylation.
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: All the authors of this manuscript consent to its publication as a research article in BMC Biology. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Seib E, Klein T. The role of ligand endocytosis in Notch signalling. Biol Cell. 2021. 10.1111/boc.202100009. - PubMed
-
- Klein T. Wing disc development in the fly: the early stages. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2001;11:470–5. - PubMed
-
- del Álamo D, Rouault H, Schweisguth F. Mechanism and significance of cis-inhibition in Notch signalling. Curr Biol. 2011;21:R40–47. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

