Biodegradable Chelating Agents for Effective CaSO4 Scale Removal in Oil and Gas Production
- PMID: 41179210
- PMCID: PMC12573150
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.5c06982
Biodegradable Chelating Agents for Effective CaSO4 Scale Removal in Oil and Gas Production
Abstract
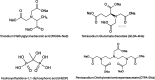
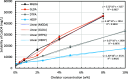
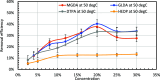
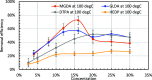
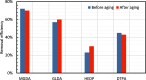
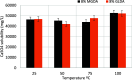
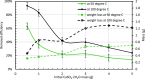
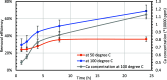
CaSO4 mineral scale is a persistent flow assurance challenge in oil and gas production. Usually, high concentrations of chelating agent formulations are used to dissolve scale deposits formed in surface flow lines and downhole. However, many conventional aminopolycarboxylates (APCAs) could raise health and environmental concerns. On the other hand, biodegradable chelators are often regarded as less efficient and less cost-effective for scale removal. This work compares the performance of two biodegradable chelators, methylglycine diacetic acid (MGDA) and l-glutamic acid N,N-diacetic acid (GLDA), with the nondegradable diethylenetriamine pentaacetic acid (DTPA) and 1-hydroxyethane-1,1-diphosphonic acid (HEDP), in dissolving CaSO4·2H2O crystals at elevated temperatures. Results shows that MGDA is highly effective and has strong potential to replace traditional chelators. The scale removal efficiency followed the order of MGDA > GLDA > DTPA > HEDP across concentrations at 25 °C, 50 °C, and 100 °C, respectively. With 16% MGDA and pH 10, more than 80% CaSO4·2H2O was removed at 100 °C with a solid/solution ratio of 2 g/10 mL. The scale removal efficiency of MGDA exceeded that of GLDA (66%), DTPA (45%), and HEDP (25%) at the optimal pH. Through characterizations of the dispersed solids in chelator solutions using X-ray diffraction, it is concluded that the dissolving mechanism involves direct interactions between Ca2+ and the chelating agents, along with minor formation of Ca-(OH)2 particles at optimized alkaline conditions. Overall, this work demonstrated MGDA and GLDA as effective biodegradable alternatives for CaSO4 removal in the oil and gas industry.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Figures


References
-
- Mohammed I., Svenningsen S. W., Kamounah F. S., Chen T., Pittelkow M., Sølling T. I., Mahmoud M.. Calcium sulfate scale: A review of state-of-the-art. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2024;242:213228. doi: 10.1016/j.geoen.2024.213228. - DOI
-
- Van Driessche A. E. S., Stawski T. M., Kellermeier M.. Calcium sulfate precipitation pathways in natural and engineered environments. Chem. Geol. 2019;530:119274. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2019.119274. - DOI
-
- Chen S., Aljeaban N. A., Huang T., Chen T.. Synthesis and evaluation of scale inhibitors for squeeze treatment of carbonate reservoir. Desalination. 2025;607:118807. doi: 10.1016/j.desal.2025.118807. - DOI
-
- Børeng, R. ; Chen, P. ; Hagen, T. ; Sitz, C. ; Thoraval, R. ; Kotlar, H. K. . Creating Value with Green Barium Sulphate Scale DissolversDevelopment and Field Deployment on Statfjord Unit. In SPE International Symposium on Oilfield Scale, 2004.
-
- Jordan M. M., Graham G. M., Sorbie K. S., Matharu A., Tomlins R., Bunney J.. Scale Dissolver Application: Production Enhancement and Formation-Damage Potential. SPE Prod. Facil. 2000;15(04):288–295. doi: 10.2118/66565-PA. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
