Aperiodic brain activity changes in patients with stroke following virtual reality-based upper limb robotic rehabilitation: a pilot Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 41179260
- PMCID: PMC12575235
- DOI: 10.3389/fnhum.2025.1671804
Aperiodic brain activity changes in patients with stroke following virtual reality-based upper limb robotic rehabilitation: a pilot Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
Introduction: Stroke-related brain changes have traditionally been studied through oscillatory electroencephalographic (EEG) activity, but recent evidence highlights the value of aperiodic components. This pilot randomized controlled trial aimed to assess stroke-related aperiodic EEG changes following virtual reality-based robotic rehabilitation using the Spectral Exponent Index (SEI).
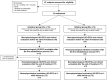
Methods: Nineteen patients with subacute stroke were randomized to unilateral (n = 9) or bilateral (n = 10) upper limb training with a robotic exoskeleton (30 sessions). EEG was recorded at rest before (T0), after (T1), and at 1-week follow-up (T2). SEI was computed for hemispheric and sensorimotor clusters, in affected (AH) and unaffected (UH) hemispheres. Clinical evaluation was performed at T0 and T1 with validated clinical scales.
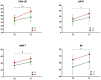
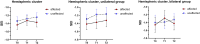
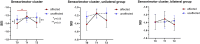
Results: At T0, the SEI in the sensorimotor cluster of the AH was significantly lower than in the UH. At T1, the SEI in the AH increased together with clinical improvements in upper limb motor function. At T2, the SEI in the AH decreased again and was lower than in the UH. No differences were found between unilateral and bilateral groups.
Discussion: Robotic rehabilitation modulated the aperiodic EEG background in the affected hemisphere of patients with stroke, particularly in sensorimotor areas. These SEI changes mirrored motor recovery, suggesting that it may represent a useful biomarker to track localized neural mechanisms of functional improvement after stroke. No differences between unilateral and bilateral training likely reflect the pilot sample size or shared cortical mechanisms of action activated by both rehabilitation approaches.
Clinical trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov registration number: NCT05176600.
Keywords: Spectral Exponent Index (SEI); quantitative electroencephalography (QEEG); rehabilitation; robotics; virtual reality (VR).
Copyright © 2025 Mauro, Fasano, Germanotta, Cortellini, Insalaco, Pavan, Comanducci, Guglielmelli and Aprile.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Ajčević M., Furlanis G., Miladinović A., Buoite Stella A., Caruso P., Ukmar M., et al. (2021). Early EEG alterations correlate with CTP hypoperfused volumes and neurological deficit: a wireless EEG Study in hyper-acute ischemic stroke. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 49, 2150–2158. 10.1007/s10439-021-02735-w - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

