Unmasking TRALI: a case report of multiple myeloma and transfusion-associated event
- PMID: 41181452
- PMCID: PMC12578070
- DOI: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000003729
Unmasking TRALI: a case report of multiple myeloma and transfusion-associated event
Abstract
Introduction and importance: Transfusion-related acute lung injury (TRALI) is a relatively rare but severe respiratory complication that can occur following the transfusion of blood products. Despite its infrequent occurrence, TRALI is a leading cause of transfusion-related mortality, underscoring the need for rapid diagnosis and appropriate management. However, diagnosis remains challenging due to its clinical overlap with other causes of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).
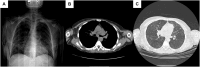
Case presentation: This report describes the case of a 57-year-old woman with multiple myeloma (MM) who developed acute respiratory distress consistent with TRALI 4 hours after receiving a whole blood transfusion for severe pancytopenia.
Clinical discussion: This case highlights the diagnostic difficulties in distinguishing TRALI from other post-transfusion complications, including transfusion-associated circulatory overload (TACO), allergic reactions, cardiac complications, and infectious processes. It also emphasizes the need for a high index of suspicion in susceptible patients. We discuss the potential risk factors, underlying pathophysiology, and essential elements of the differential diagnosis.
Conclusion: Increased awareness and early recognition of TRALI are essential for improving patient outcomes. Moreover, this case aligns with the existing literature by highlighting the diagnostic challenges and the importance of considering TRALI in patients with hematological malignancies who require transfusion support.
Keywords: TRALI; blood transfusion; case report; multiple myeloma; transfusion-related acute lung injury.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Sponsorships or competing interests that may be relevant to content are disclosed at the end of this article. The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- White SK, Schmidt RL, Walker BS, et al. The epidemiology of transfusion-related acute lung injury: a scoping review and analysis. Transfusion 2023;63:104–16. - PubMed
-
- Semple JW, Rebetz J, Kapur R. Transfusion-associated circulatory overload and transfusion-related acute lung injury. Blood 2019;133:1840–53. - PubMed
-
- Riaz AA, Ginimol M, Rasha R, et al. Transparency in the reporting of artificial intelligence – the TITAN guideline. Prem J Sci 2025;10:100082.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
