Prediction of hemorrhagic transformation in acute ischemic stroke patients using clinico-radiomics models
- PMID: 41188459
- PMCID: PMC12586621
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-22469-2
Prediction of hemorrhagic transformation in acute ischemic stroke patients using clinico-radiomics models
Abstract
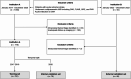
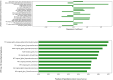
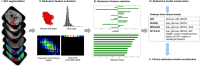
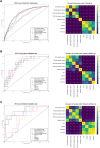
This study aimed to develop and validate a clinico-radiomics model integrating radiomics features from multiparametric MRI and clinical scoring systems to predict hemorrhagic transformation (HT) in acute ischemic stroke. A total of 918 patients were retrospectively included. Patients from Institution A who underwent MRIs between 2017 and 2019 were assigned to the training set (n = 792), whereas those from 2020 (n = 78) formed the internal validation set. External validation included 48 patients from Institution B. All patients underwent multiparametric MRI, including diffusion- and perfusion-weighted imaging, fluid-attenuated inversion recovery, and gradient-echo. Radiomics features were selected using the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator regression and random forest models. Clinico-radiomics models were developed using logistic regression by combining radiomics features with clinical scoring systems (HAT, SEDAN, DRAGON, SITS-ICH). Model performance was assessed using the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC), with DeLong's test for comparison. Ten radiomics features were selected: time-to-peak, mean transit time, time-to-maximum, relative cerebral blood volume, and relative cerebral blood flow. The radiomics model demonstrated comparable performance to clinical models in the internal validation set (AUC: 0.79 vs. 0.75-0.81); but outperformed them in the external validation set (AUC: 0.85 vs. 0.66-0.68). Clinico-radiomics models demonstrated higher AUCs than radiomics or clinical models in both internal (AUC: 0.81-0.84 vs. 0.79 vs. 0.75-0.81) and external validation sets (AUC: 0.86-0.89 vs. 0.85 vs. 0.66-0.68). These findings suggest that clinico-radiomics models offer improved predictive accuracy for HT compared to radiomics or clinical scoring models alone.
Keywords: Acute ischemic stroke; Hemorrhagic transformation; Magnetic resonance imaging; Perfusion; Radiomics.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Yaghi, S. et al. Treatment and outcome of hemorrhagic transformation after intravenous alteplase in acute ischemic stroke: A scientific statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke48, e343–e361. 10.1161/STR.0000000000000152 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Paciaroni, M. et al. Early hemorrhagic transformation of brain infarction: rate, predictive factors, and influence on clinical outcome: results of a prospective multicenter study. Stroke39, 2249–2256. 10.1161/STROKEAHA.107.510321 (2008). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

