Sustainable care quality improvement: a scoping literature review of performance measurement in lean healthcare implementations
- PMID: 41204235
- PMCID: PMC12595819
- DOI: 10.1186/s12913-025-13598-5
Sustainable care quality improvement: a scoping literature review of performance measurement in lean healthcare implementations
Abstract
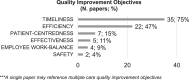
Background: The phenomenon of demographic changes and the aging population requires Territorial Ambulatory Healthcare (TAH) to provide increasingly high-quality and sustainable care to a growing number of individuals with chronic diseases. In this context, Healthcare Lean Management (HLM) can support sustainable care quality, increasing patient satisfaction and process performance. According to the literature, a significant barrier to sustainability is the limitation of monitoring systems for process performance. For this reason, this study aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the most pursued improvement objectives, performance measurement indicators, and data collection tools and techniques of HLM implementations within TAH.
Methods: Following the PRISMA protocol, a scoping literature review was conducted to investigate the linkages among improvement objectives, performance measurement indicators, and data collection tools and techniques.
Results: The current study provides valuable insights into the performance measurement indicators that should be adopted according to the specific improvement objectives. It highlights that measuring and monitoring are essential activities but often overlooked in HLM projects, negatively affecting the effectiveness of this managerial approach in terms of sustainability over time.
Conclusions: The final results demonstrate how research about performance measurement systems in HLM projects is still in its early stages, both from a theoretical and empirical perspective. The current research enriches the knowledge about the theme and provides managerial support to the journey of territorial care services toward sustainable care quality.
Supplementary Information: The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1186/s12913-025-13598-5.
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization, & United Nations Children’s Fund. Operational framework for primary health care: transforming vision into action. 2020.
-
- World Health Organization. Long-term care for older people: package for universal health coverage. 2024.
-
- World Health Organization. World report on ageing and health. 2015.
-
- World Health Organization & United Nations Children’s Fund, 2018. Primary health care measurement framework and indicators: monitoring health systems through a primary health care lens. World Health Organ. 2022.
-
- World Health Organization. Continuity and coordination of care: a practice brief to support implementation of the WHO framework on integrated people-centred health services. 2018.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources