MiDNE a tool for Multi-omics genes and drugs interactions discovery
- PMID: 41209342
- PMCID: PMC12593681
- DOI: 10.1016/j.csbj.2025.10.022
MiDNE a tool for Multi-omics genes and drugs interactions discovery
Abstract
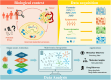
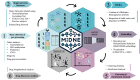
The availability of models representing molecular interactions in complex pathologies is essential for understanding their molecular setup and identifying therapeutic vulnerabilities. In this context, the advent of high-throughput technologies has enabled the rapid and cost-effective profiling of multiple omics layers, driving a paradigm shift from generalized models to disease-specific, context-aware modeling approaches. While the analysis of individual omics layers can provide information about specific aspects of cellular biology for a given disease, it often fails to capture complex interactions among molecules and drugs operating across different regulatory levels. Here, we introduce MiDNE (Multi-omics genes and Drugs Network Embedding), a novel computational framework that integrates experimental multi-omics data with pharmacological knowledge to uncover disease specific multi-omics gene and drug interactions. MiDNE integrates omics-specific networks, derived from experimental data, with known drug interactors in a multiplex heterogeneous network. It applies a network embedding procedure based on the random walk with restart algorithm to project genes and drugs into a shared multi-omics latent space, enabling gene-drug clustering and neighborhood search. We demonstrate the potential of MiDNE on Breast Invasive Carcinoma and Glioblastoma multiforme, by integrating gene expression, methylation, proteomic, and copy number variation profiles with curated drug-target interactions. By providing multilayer and disease-specific views of gene and drug interactions, MiDNE facilitates the discovery of actionable gene-drug relationships and the development of precision pharmacological strategies. MiDNE is available as both an open-source R package and a Shiny web application.
Keywords: Cancer research; Drug discovery; Multi-omics data integration; R package; Systems biology.
© 2025 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Wang B., Mezlini A.M., Demir F., Fiume M., Zhuowen T., et al. Similarity network fusion for aggregating data types on a genomic scale. Nat Methods. 2014;11(3):333–337. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
