GLObal Solar Wind Structure (GLOWS)
- PMID: 41210206
- PMCID: PMC12589363
- DOI: 10.1007/s11214-025-01233-y
GLObal Solar Wind Structure (GLOWS)
Abstract
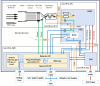
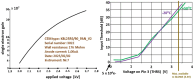
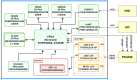
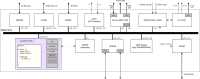
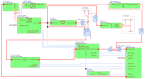
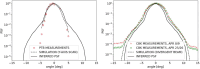
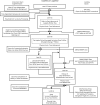
Information on the evolution of latitudinal profiles of the solar wind speed and density is one of the important elements needed to understand global observations of heliospheric neutral and charged particle populations performed by NASA's integrated heliospheric observatory Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe (IMAP). This information is provided by the GLObal solar Wind Structure (GLOWS) experiment. GLOWS is a single-pixel Lyman- photometer that observes the heliospheric backscatter glow emitted by interstellar neutral (ISN) H inside the heliosphere, illuminated by the solar Lyman- emission. GLOWS features a specially designed optical entrance system with a baffle, collimator, and interference filter; a channeltron-based photon event detector; a digital processing unit (DPU) with custom-designed software that registers photon events and assembles lightcurves; a front-end electronics block that interfaces the detector and DPU; and the necessary power and voltage distribution system. Due to charge-exchange between ISN H and the solar wind, the helioglow bears imprints of the solar wind structure. Analysis of lightcurves observed daily along Sun-centered circles with a 75° radius in the sky yields profiles of intensities of the charge exchange reaction, which are decomposed into solar wind speed and density profiles at a Carrington period cadence. With them, it is possible to infer the shape of the heliosphere and its variation during the solar cycle and to determine the attenuation through re-ionization of energetic neutral atom fluxes between the ENA creation sites in the inner heliosheath and the IMAP ENA detectors.
© The Author(s) 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing InterestsThe authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Figures










References
-
- Baliukin II, Bertaux J-L, Quémerais E, Izmodenov VV, Schmidt W (2019) SWAN/SOHO Lyman- mapping: the hydrogen geocorona extends well beyond the moon. J Geophys Res 124:861–885. 10.1029/2018JA026136 - DOI
-
- Baliukin I, Bertaux JL, Bzowski M, Izmodenov V, Lallement T, Provornikova E, Quémerais E (2022) Backscattered solar Lyman- emission as a tool for the heliospheric boundary exploration. Space Sci Rev 218:45. 10.1007/s11214-022-00913-3. arXiv:2206.15175 [astro-ph.SR] - DOI
-
- Barciński T, Kosturek R, Kowalski T, Bzowski M, Wawrzaszek R, Mostowy K, et al. (2024) The effect of the coating process thermal cycle on mechanical properties of AA6061-T6 used for load-carrying elements of a space instrument: a case study. Bull Pol Acad Sci 72(5):e150338. 10.24425/bpasts.2024.150338 - DOI
-
- Bertaux JL, Kyrölä E, Quémerais E, Pellinen R, Lallement R, Schmidt W, et al. (1995) SWAN: a study of solar wind anisotropies on SOHO with Lyman Alpha sky mapping. Sol Phys 162(1–2):403–439. 10.1007/BF00733435 - DOI
-
- Bertaux JL, Lallement R, Quémerais E (1996) UV studies and the solar wind. Space Sci Rev 78:317–328. 10.1007/BF00170818 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
