circHERC1-A telomerase activator
- PMID: 41223261
- PMCID: PMC12609087
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adz3680
circHERC1-A telomerase activator
Abstract
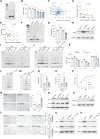
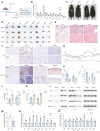
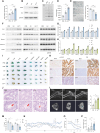
Telomerase, crucial for maintaining telomere integrity and genomic stability, is typically silenced in somatic cells with advancing age. In this study, we identify circHERC1 as a regulator of telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT) transcription. Specifically, circHERC1 binds to the TERT promoter, facilitating the recruitment of RNA polymerase II and c-Fos, thereby activating TERT expression. Notably, circHERC1 expression exhibits a decline with age, which correlates with reduced telomerase activity. Restoration of circHERC1 expression enhances telomerase activity, promotes telomere elongation, and reverses aging-associated phenotypes. Furthermore, delivery of circHERC1 using adeno-associated virus vectors or extracellular vesicles effectively restores telomerase activity, preserves telomere integrity, and mitigates senescence. This intervention leads to improvements in cognitive function, physical performance, and a reduction in inflammation. These findings highlight the important role of circHERC1 in telomerase regulation and the aging process, positioning it as a potential therapeutic target for antiaging interventions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Gorgoulis V., Adams P. D., Alimonti A., Bennett D. C., Bischof O., Bishop C., Campisi J., Collado M., Evangelou K., Ferbeyre G., Gil J., Hara E., Krizhanovsky V., Jurk D., Maier A. B., Narita M., Niedernhofer L., Passos J. F., Robbins P. D., Schmitt C. A., Sedivy J., Vougas K., von Zglinicki T., Zhou D., Serrano M., Demaria M., Cellular senescence: Defining a path forward. Cell 179, 813–827 (2019). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

