Strengthening the reporting of observational studies in epidemiology using Mendelian randomization (STROBE-MR): a Korean translation of explanation and elaboration
- PMID: 41223895
- PMCID: PMC12611437
- DOI: 10.12771/emj.2025.00934
Strengthening the reporting of observational studies in epidemiology using Mendelian randomization (STROBE-MR): a Korean translation of explanation and elaboration
Abstract
멘델 무작위화(Mendelian randomization, MR) 연구는 조절 가능한 노출(modifiable exposure)이 건강결과에 미치는 인과효과(causal effect)를 더 잘 이해하게 해 주지만, 그 근거는 종종 보고가 불충분함으로 인하여연구 결과의 해석과 적용에 한계가 있을 수 있다. 보고지침은 흔히 무슨 연구를 하고 무엇을 발견했는지 독자가 쉽게 이해하도록 돕는다. STROBE-MR(관찰연구의 멘델 무작위화를 활용한 보고지침)은 MR 연구를 명확하고 투명하게 보고하도록 돕는다. STROBE-MR을 논문 작성에 활용하면 독자, 심사자, 학술지 편집인이 MR 연구의 보고 품질과 완성도를 평가하는 데 도움이 될 것이다. 이 글은 STROBE-MR 체크리스트 20개 항목의 의미와 근거를 설명하고, 각 항목마다 사례를 제시해 독자가 잘 이해할 수 있는 논문 작성법을 설명하려고 하였다.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form at
Figures
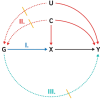
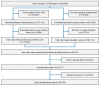
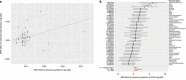
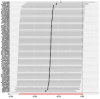
References
-
- Smith GD, Ebrahim S. Data dredging, bias, or confounding. BMJ. 2002;325:1437–1438. doi: 10.1136/bmj.325.7378.1437. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.325.7378.1437 . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lawlor DA, Davey Smith G, Kundu D, Bruckdorfer KR, Ebrahim S. Those confounded vitamins: what can we learn from the differences between observational versus randomised trial evidence? Lancet. 2004;363:1724–1727. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(04)16260-0. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(04)16260-0 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Taubes G. Epidemiology faces its limits. Science. 1995;269:164–169. doi: 10.1126/science.7618077. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.7618077 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sattar N, Preiss D. Reverse causality in cardiovascular epidemiological research: more common than imagined? Circulation. 2017;135:2369–2372. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.028307. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.028307 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ortola R, Garcia-Esquinas E, Soler-Vila H, Ordovas JM, Lopez-Garcia E, Rodriguez-Artalejo F. Changes in health status predict changes in alcohol consumption in older adults: the Seniors-ENRICA cohort. J Epidemiol Community Health. 2019;73:123–129. doi: 10.1136/jech-2018-211104. https://doi.org/10.1136/jech-2018-211104 . - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

