Sumac Polyphenols as Pan-Herpesvirus Inhibitors
- PMID: 41226438
- PMCID: PMC12607321
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms262110398
Sumac Polyphenols as Pan-Herpesvirus Inhibitors
Abstract
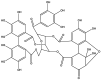
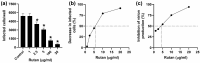
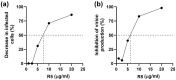
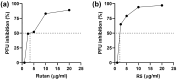
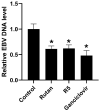
Pandemic preparedness is a complex of threat-agnostic countermeasures developed in advance which would be efficient against a future outbreak regardless of its causative agent, and broad-spectrum antivirals constitute a critical component of this complex. Plant polyphenols are known to suppress viruses of unrelated families by acting on multiple viral and cellular structures. We therefore searched for broad-spectrum antivirals among polyphenols that have been confirmed as safe to humans. The ellagitannin geraniin and galloylglucose constituents of the drug Rutan (1,2,3,4,6-penta-O-galloyl-β-D-glucose [R5], 3-bis-O-galloyl-1,2,4,6-tetra-O-galloyl-β-D-glucose [R6], 2,4-bis-O-galloyl-1,3,6-tri-O-galloyl-β-D-glucose [R7], 2,3,4-bis-O-galloyl-1,6-di-O-galloyl-β-D-glucose [R8]) were isolated from Geranium sanguineum and sumac (Rhus coriaria), respectively. We revealed their activity towards herpes simplex viruses (HSV-1 and HSV-2), human cytomegalovirus (CMV), and the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). R5 suppressed HSV-1 and HSV-2 with equal efficiency, while Rutan and R7 were more active against HSV-1, and geraniin against HSV-2. Rutan and R5 also inhibited the intracellular replication of CMV and EBV (contrary to our expectations, geraniin and polyphenols R6-R8 showed no activity). Thus, we have shown for the first time that sumac polyphenols are capable of suppressing-in addition to HIV, influenza virus, and SARS-CoV-2-the reproduction of representatives of all three Orthoherpesviridae subfamilies, meeting the criteria for further development as broad-spectrum antivirals.
Keywords: Epstein–Barr virus; SARS-CoV-2; cytomegalovirus; geranium; herpes simplex virus type 1; herpes simplex virus type 2; influenza A virus; polyphenols; sumac.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of this study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of the data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures



References
-
- Kaye A.D., Okeagu C.N., Pham A.D., Silva R.A., Hurley J.J., Arron B.L., Sarfraz N., Lee H.N., Ghali G.E., Gamble J.W., et al. Economic impact of COVID-19 pandemic on healthcare facilities and systems: International perspectives. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Anaesthesiol. 2021;35:293–306. doi: 10.1016/j.bpa.2020.11.009. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Robinson P.C., Liew D.F.L., Tanner H.L., Grainger J.R., Dwek R.A., Reisler R.B., Steinman L., Feldmann M., Ho L.P., Hussell T., et al. COVID-19 therapeutics: Challenges and directions for the future. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2022;119:e2119893119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2119893119. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

