Xanthohumol Alters Gut Microbiota Metabolism and Bile Acid Dynamics in Gastrointestinal Simulation Models of Eubiotic and Dysbiotic States
- PMID: 41226734
- PMCID: PMC12608232
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms262110698
Xanthohumol Alters Gut Microbiota Metabolism and Bile Acid Dynamics in Gastrointestinal Simulation Models of Eubiotic and Dysbiotic States
Abstract
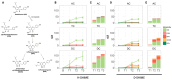
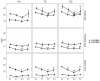
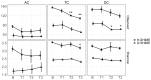
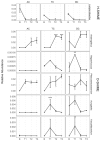
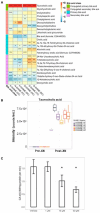
Xanthohumol (XN), a polyphenol from hops (Humulus lupulus), exhibits antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antihyperlipidemic, and chemo-preventive activity. Preclinical evidence suggests gut microbiota are critical to mediating some of these bioactivities. Nevertheless, its precise impact on human gut microbiota, particularly at supplemental doses, remains poorly characterized. We evaluated 200 mg/day XN for 3 weeks on human gut microbiota in a eubiotic and dysbiotic model using the Simulator of the Human Intestinal Microbial Ecosystem (SHIME®). Functional assessments of microbiota included quantification of XN metabolites, short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), and untargeted metabolomics of the digestive metabolome. Bacterial composition was assessed by 16S rRNA gene sequencing. XN reduced alpha-diversity and short-chain fatty acid production in both models, as well as altered taxa abundance variably between models. XN disrupted bile acid metabolism through inhibition of microbial bile salt hydrolase (BSH). The modulation of bile acid metabolism has important implications for host-level bioactivity of XN.
Keywords: Humulus lupulus; SHIME; bile acids; dysbiosis; gut microbiota; phytochemical; polyphenol; xanthohumol.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Dietz B.M., Kang Y.-H., Liu G., Eggler A.L., Yao P., Chadwick L.R., Pauli G.F., Farnsworth N.R., Mesecar A.D., van Breemen R.B., et al. Xanthohumol Isolated from Humulus Lupulus Inhibits Menadione-Induced DNA Damage through Induction of Quinone Reductase. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2005;18:1296–1305. doi: 10.1021/tx050058x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Paraiso I.L., Tran T.Q., Magana A.A., Kundu P., Choi J., Maier C.S., Bobe G., Raber J., Kioussi C., Stevens J.F. Xanthohumol Ameliorates Diet-Induced Liver Dysfunction via Farnesoid X Receptor-Dependent and Independent Signaling. Front. Pharmacol. 2021;12:643857. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.643857. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhang Y., Bobe G., Revel J.S., Rodrigues R.R., Sharpton T.J., Fantacone M.L., Raslan K., Miranda C.L., Lowry M.B., Blakemore P.R., et al. Improvements in Metabolic Syndrome by Xanthohumol Derivatives Are Linked to Altered Gut Microbiota and Bile Acid Metabolism. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2020;64:1900789. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201900789. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

