Emerging Thrombolysis Technologies in Vascular Thrombosis
- PMID: 41227154
- PMCID: PMC12607982
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm14217758
Emerging Thrombolysis Technologies in Vascular Thrombosis
Abstract
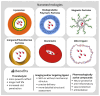
Background/Objectives: Thrombotic diseases, such as ischemic stroke, acute myocardial infarction, and venous thromboembolism, are leading causes of global morbidity and mortality. Traditional thrombolytic therapies like systemic tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) are limited by bleeding risks, poor targeting, and inconsistent efficacy. This review explores emerging non-pharmacological technologies aimed at overcoming these challenges through targeted, minimally invasive thrombolysis. Methods: A narrative synthesis of recent advancements was conducted, focusing on six innovative approaches: ultrasound-mediated thrombolysis (UMT), microrobots, electrothrombectomy, photothrombectomy, magnetic targeted thrombolysis, and nanotechnology. Preclinical and clinical studies were reviewed to assess mechanisms, efficacy, safety, and translational potential, prioritizing technologies with demonstrated success in animal or early human trials. Results: Technologies like microbubble-enhanced UMT, magnetically actuated microrobots, and fibrin-targeted nanoparticles showed promising results. UMT improved recanalization in ischemic stroke and pulmonary embolism, while electrothrombectomy demonstrated safe, effective clot extraction in human trials. However, challenges remain in scalability, biocompatibility, and clinical integration, with microrobots and photothrombectomy still in preclinical stages. Conclusions: Emerging thrombolysis technologies offer safer, more targeted alternatives to conventional treatments. Clinical adoption will depend on overcoming translational hurdles, including large-scale trials, miniaturization, and interdisciplinary collaboration, with a focus on hybrid approaches and real-time imaging integration.
Keywords: electromechanical; magnetic; microbots; nanoparticles; phototherapy; thrombolysis; thrombosis; ultrasound.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Raskob G.E., Angchaisuksiri P., Blanco A.N., Buller H., Gallus A., Hunt B.J., Hylek E.M., Kakkar A., Konstantinides S.V., McCumber M., et al. Thrombosis: A major contributor to global disease burden. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2014;34:2363–2371. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.114.304488. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

