SGLT2-is in Acute Heart Failure
- PMID: 41227196
- PMCID: PMC12608667
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm14217799
SGLT2-is in Acute Heart Failure
Abstract
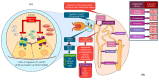
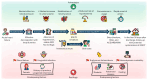
Despite the wealth of evidence in favour of SGLT2 inhibitor use in patients with chronic heart failure, their role in the very early stages of heart failure is still unclear. While the latest update of the European Society of Cardiology guidelines on heart failure advocates the use SGLT2 inhibitors in the acute phases of heart failure based on the results of the latest trials, it does not clarify the appropriate timing to start this therapy, leaving the clinician to decide whether SGLT2 inhibitors should be started directly during hospitalization or at discharge. Conversely, the recently published focused update of the American College of Cardiology expert consensus decision pathway on the clinical assessment, management, and trajectory of patients hospitalized with heart failure clearly supports the safety and early clinical benefit use of SGLT2 inhibitors based on evidence coming from the EMPULSE and SOLOIST-WHF trials. The expert consensus decision pathway states that SGLT2 inhibitors can be initiated regardless of left ventricular ejection fraction at any time during hospitalization and places a greater emphasis on implementing the other pillars of therapy for heart failure with reduced ejection fraction after stabilization. Moreover, the results of the very recent DAPA ACT HF-TIMI 68 trial on dapagliflozin in patients with acute heart failure, although limited by a follow-up of only 2 months, did not show a reduction in mortality or heart failure hospitalizations. Based on the currently available published data, we will review what is already known about the use of these drugs in the early phases of acute heart failure and analyze their pathophysiological rationale from a practical perspective.
Keywords: SGLT2i; acute heart failure; decongestion.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Korytkowski M.T., Muniyappa R., Antinori-Lent K., Donihi A.C., Drincic A.T., Hirsch I.B., Luger A., McDonnell M.E., Murad M.H., Nielsen C., et al. Management of Hyperglycemia in Hospitalized Adult Patients in Non-Critical Care Settings: An Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022;107:2101–2128. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgac278. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

