Analysis of the Bioactive Compounds and Physiological Activities of Commonly Consumed Noni Juice in Republic of Korea
- PMID: 41227701
- PMCID: PMC12607524
- DOI: 10.3390/foods14213732
Analysis of the Bioactive Compounds and Physiological Activities of Commonly Consumed Noni Juice in Republic of Korea
Abstract
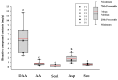
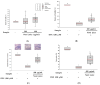
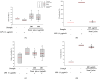
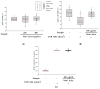
Noni (Morinda citrifolia L.) juice is increasingly recognized for its potential health-promoting properties. In this research, the bioactive compounds and physiological effects of commercial noni juice products in Korea were assessed. Noni juice was found to contain high levels of total phenolics (6.39 ± 1.45 mg gallic acid equivalents (GAE)/g) and proanthocyanidins (8.64 ± 6.20 mg catechin equivalents (CE)/g). Furthermore, it exhibited potent antioxidant activities, with 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) and 2,2'-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) diammonium salt (ABTS) radical scavenging activities of 44.03 ± 14.88% and 55.91 ± 2.62%, respectively, which exceeded those reported for common fruit juices such as apple, orange, and blueberry. Additionally, noni juice reduced lipid accumulation by 5.92% and reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels by 7.23% in 3T3-L1 adipocytes; improved fusion index to 81.44% and restored myotube diameter by 37.24% in dexamethasone-induced C2C12 cells; and suppressed LPS-induced nitric oxide (NO) production. These results suggested that noni juice has anti-inflammatory, anti-obesity, anti-muscle atrophy, and antioxidant properties, supporting its potential as a functional health beverage.
Keywords: bioactive compounds; noni (Morinda citrifolia L.); noni juice; physiological activities.
Conflict of interest statement
Do Sang Lee and Im-Joung La were employed by Atomy R&D Center. Jae-Yeon Lee and Eun Young Park were employed by NSTBIO Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The authors declare that this study received funding from the 2024 Research Grant from the NSTBIO Co., Ltd. and Atomy R&D Center. The funder had the following involvement with the study: Resources, Validation, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Conceptualization, and Writing—review and editing.
Figures


References
-
- Westendorf J., Mettlich C. The benefits of noni juice: An epidemiological evaluation in Europe. J. Med. Food Plants. 2009;1:64–79.
-
- Ali M., Kenganora M., Manjula S.N. Health benefits of Morinda citrifolia (Noni): A review. Pharmacogn. J. 2016;8:321–334. doi: 10.5530/pj.2016.4.4. - DOI
-
- Kim Y., Pyeon J., Lee J.Y., Kim E.M., La I.J., Lee O.H., Kim K., Sung J., Kim Y. Chemical fingerprint analysis of fermented Morinda citrifolia L.(Noni) juice by UHPLC Q-TOF/MS combined with chemometric analysis. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2024;67:59. doi: 10.1186/s13765-024-00910-w. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

