Self-Supported Polyhedral-like Co3S4 Nanostructures Enabling Efficient High Current Hydrogen Evolution Reaction
- PMID: 41227983
- PMCID: PMC12608485
- DOI: 10.3390/ma18215025
Self-Supported Polyhedral-like Co3S4 Nanostructures Enabling Efficient High Current Hydrogen Evolution Reaction
Abstract
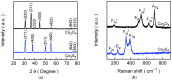
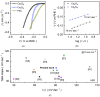
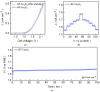
The advancement of overall water-splitting technologies relies on the development of earth-abundant electrocatalysts that efficiently produce H2 as a chemical fuel while offering high catalytic efficiency, structural robustness, and low-cost synthesis. Therefore, we aim to develop a cost-effective and durable non-noble electrocatalyst for overall water splitting. A straightforward hydrothermal approach was employed to fabricate freestanding polyhedral Co3O4 on a microporous Ni foam scaffold, followed by anion-exchange transformation in the presence of Na2S solution to yield its conductive sulfide analog. The engineered Co3S4 electrode delivers remarkable HER activity in 1.0 M KOH, requiring a low overpotential (<100 mV) to drive 10 mA cm-2, far outperforming its pristine oxide counterpart and even closely benchmarking with a commercial Pt/C catalyst. This exceptional performance is governed by the synergistic effects of enhanced electrical conductivity, abundant catalytic sites, and accelerated charge-transfer kinetics introduced through sulfur substitution. Furthermore, the optimized Co3S4 electrodes enable a bifunctional overall water-splitting device that achieves a cell voltage of >1.76 V at 100 mA cm-2 and maintains prolonged operational stability for over 100 hrs. of continuous operation. Post-stability analyses confirm insignificant phase preservation during testing, ensuring sustained activity throughout the electrolysis process. This study highlights the potential of anion-exchanged Co3S4 as a cost-effective and durable catalyst for high-performance HER and full-cell water-splitting applications.
Keywords: Co3S4; anion-exchange; hydrogen evolution reaction; hydrothermal synthesis; overall-water electrolysis; polyhedral structure.
Conflict of interest statement
Author Abu Saad Ansari was employed by the company Nano Center Indonesia Research Institute. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Yue M., Lambert H., Pahon E., Roche R., Jemei S., Hissel D. Hydrogen energy systems: A critical review of technologies, applications, trends and challenges. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021;146:111180. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2021.111180. - DOI
-
- Cherp A., Vinichenko V., Tosun J., Gordon J.A., Jewell J. National growth dynamics of wind and solar power compared to the growth required for global climate targets. Nat. Energy. 2021;6:742–754. doi: 10.1038/s41560-021-00863-0. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

