Revisiting p53 Immunohistochemical Staining and Its Prognostic Implications in Advanced EGFR-Mutated Lung Adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 41228367
- PMCID: PMC12608574
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers17213577
Revisiting p53 Immunohistochemical Staining and Its Prognostic Implications in Advanced EGFR-Mutated Lung Adenocarcinoma
Abstract
Background/objectives: TP53 mutations in advanced epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-mutated non-small cell lung cancer could worsen prognosis. Therefore, we aimed to investigate the clinical significance of TP53 mutations and p53 expression in these patients.
Methods: Patients with advanced/metastatic EGFR-mutated lung adenocarcinoma treated with first-line tyrosine kinase inhibitors were retrospectively enrolled. Sanger sequencing was performed to detect TP53 mutations and immunohistochemical staining was used to verify p53 protein expression levels. Kaplan-Meier and Cox proportional hazards analyses were used to estimate survival and hazard ratio (HR) with 95% confidence interval (CI).
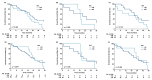
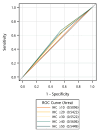
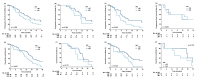
Results: The study involved 83 patients with adequate tumor samples for TP53/p53 analysis. Patients with tumor p53 immunostaining ≥50% showed significantly better overall survival (OS) (HR: 0.49 [95% CI: 0.30-0.81], p < 0.001), but TP53 mutations were not associated with inferior progression-free survival (PFS) or OS (missense vs. wild-type [PFS, HR: 0.68 (95% CI: 0.40-1.15), p = 0.151; OS, HR: 0.88 (95% CI: 0.56-1.42), p = 0.599]). Areas under the receiver operating characteristic curves of TP53 mutations with different cut-off values for p53 positivity were 0.51-0.56. The Kaplan-Meier survival analysis revealed significant survival benefits in patients with EGFR L858R substitution and tumor p53 immunostaining ≥50% (median PFS: 8.0 vs. 5.3; median OS: 20.4 vs. 15.3 months; log-rank p = 0.025 and 0.049, respectively).
Conclusions: Tumor p53 immunostaining (≥50%) was associated with better OS, especially in patients with TP53 mutations or L858R. Prospective clinical trials are required to explore the prognostic significance of p53 expression in the genomic era of TP53 mutations.
Keywords: Kaplan-Meier analysis; TP53 mutation; cancer; epidermal growth factor receptor; lung adenocarcinoma; p53 protein.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

