Long-term outcomes after pleural decortication for patients with chronic sterile, non-malignant pleural effusion
- PMID: 41229857
- PMCID: PMC12603448
- DOI: 10.21037/jtd-2025-1203
Long-term outcomes after pleural decortication for patients with chronic sterile, non-malignant pleural effusion
Abstract
Background: While decortication is well-established for empyema or malignancy, its role in chronic sterile, non-malignant pleural effusions (CSNMPE) remains unclear. Given the high mortality rate among patients with CSNMPE, further longitudinal studies are warranted to assess the long-term efficacy and survival outcomes associated with decortication in this population. This study assesses long-term outcomes of decortication in CSNMPE and considers implications for future management.
Methods: Between January 1, 2012, and December 31, 2022, a total of 25 patients underwent pleural decortication for CSNMPE at a single institution.
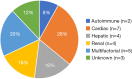
Results: Median age was 67 years, with male predominance (84%) and right-sided effusions (64%). Etiologies were cardiac (28%), multifactorial (20%), hepatic (16%), renal (16%), unknown (12%), and autoimmune (8%). The median time from initial detection of pleural effusion to decortication was 6.6 months. Minimally invasive approach was used in 52% (thoracotomy, 48%). Radiographic improvement with significant lung re-expansion (>75%) was observed in 80%, and 72% experienced symptom relief. Postoperative complications occurred in 36%. Median overall survival was 65.3 months, with 1-, 3-, and 5-year survival rates of 80.0%, 63.8%, and 50.1%, respectively. Factors associated with decreased survival included a history of cancer treatment (P<0.01), prolonged pleural effusion duration (P=0.01), and increased intraoperative blood loss (P<0.01).
Conclusions: Pleural decortication may benefit selected CSNMPE patients unresponsive to conservative therapy, offering symptom relief and survival. Findings are exploratory, and potential advantages of early intervention require further prospective validation.
Keywords: Pleura; chest tube; fibrothorax; heart failure; thoracentesis.
Copyright © 2025 AME Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://jtd.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/jtd-2025-1203/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Kim S, Park H, Cho YK, et al. Refractory Pleural Effusion in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Treated by Pleurectomy. J Rheum Dis 2017;24:43-7.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources