Effectiveness of long-acting monoclonal antibodies against laboratory-confirmed RSV in children aged < 24 months and hospitalised for severe acute respiratory infection, European pilot study, 2024 to 2025
- PMID: 41234196
- PMCID: PMC12633706
- DOI: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2025.30.45.2500816
Effectiveness of long-acting monoclonal antibodies against laboratory-confirmed RSV in children aged < 24 months and hospitalised for severe acute respiratory infection, European pilot study, 2024 to 2025
Abstract
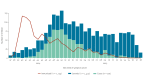
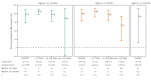
We measured effectiveness of nirsevimab against laboratory-confirmed respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infection in a test-negative case-control study among children aged < 24 months hospitalised for severe acute respiratory infection in three European countries. The overall effectiveness in the 2024/25 season among 2,201 children was 79% (95% CI: 58 to 89) and 85%, 78% and 69% at < 30, 30-89 and 90-215 days since immunisation. Immunisation was effective for preventing RSV-related hospitalisation in children, but effectiveness by time since immunisation needs monitoring in future seasons.
Keywords: Europe; RSV; monoclonal antibodies, nirsevimab, effectiveness.
Conflict of interest statement
Collaborators from the VEBIS hospital network RSV IE group: NDa reported grants from Sciensano and MSD, honoraria for lectures from Astra Zeneca, support for attending meetings from MSD, Gilead, ViiV healthcare, Eumedica (payments made to the institution), and participation in Advisory board of MSD in the past 36 months. CB reported an 8-month contract as project officer with European Public Health Association (EUPHA) in the past 36 months. SDa reported support for attending ESPID 2025 from Sanofi-Pasteur. CB, LDM, PM, SH, YD, YL, NB reported national funding for SARI surveillance from Belgian Public Services (FPS Santé Publique).
All other authors declare no conflicts of interest related to this work.
Figures
References
-
- European Medicines Agency (EMA). Beyfortus (nirsevimab). Amsterdam; EMA: Jul 2024. Available from: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/overview/beyfortus-epar-medicine-...
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) . WHO position paper on immunization to protect infants against respiratory syncytial virus disease, May 2025. Wkly Epidemiol Rec. 2025;22(100):193-218.
-
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC). Operational considerations for respiratory virus surveillance in Europe. Stockholm: ECDC; 18 Jul 2022. Available from: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/operational-consideratio...
-
- Ministerio de Sanidad (Sanidad). Recomendaciones de inmunización pasiva para prevención de enfermedad grave por VRS en la población infantil. [Passive immunization recommendations for the prevention of severe RSV disease in children]. Madrid: Sanidad; Nov 2024. Spanish. Available from: https://www.sanidad.gob.es/areas/promocionPrevencion/vacunaciones/comoTr...
-
- Direção Geral da Saúde (DGS). Imunização Sazonal contra o Vírus Sincicial Respiratório em Idade Pediátrica: Outono-Inverno 2024-2025. [Seasonal immunisation against respiratory syncytial virus in paediatric population: Autumn-Winter 2024-2025]. Lisboa: DGS; 12 Aug 2024. Portuguese. Available from: https://www.spp.pt/UserFiles/file/DOCUMENTOS%20OFICIAIS/Norma%2005_2024_...
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
