Pro-Coagulant Lipids in Physiological Ratios Found in the Activated Platelet Membrane Do Not Impact Clot Structure or Fibrinolysis in Purified Assays
- PMID: 41235326
- PMCID: PMC12607800
- DOI: 10.2147/JBM.S527558
Pro-Coagulant Lipids in Physiological Ratios Found in the Activated Platelet Membrane Do Not Impact Clot Structure or Fibrinolysis in Purified Assays
Abstract
Purpose: A central role for the pro-coagulant membrane comprising aminophospholipids (aPL) and enzymatically oxidized phospholipids (eoxPL) in promoting hemostasis via interaction with coagulation factor Gla domains is well established. However, little is known about their interactions with the fibrinolytic pathway, their ability to alter clot structure or to support the activated protein C (APC) pathway. Previous studies used membrane liposome compositions that differ from those expected physiologically and/or generated inconsistent findings. To address this, pro-coagulant membranes comprising physiological proportions of aPL and eoxPL will be tested for their ability to support fibrinolysis using standard assays.
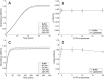
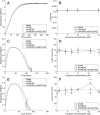
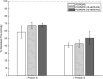
Methods: The impact of phospholipids on clot structure and clot lysis was tested using absorbance-based assays. To investigate the impact of PS or eoxPL on fibrinolysis, plasmin was monitored chromogenically, and clot dissolution measured in a purified lysis system activated by tissue plasminogen activator or urokinase. To determine the impact of eoxPL on APC/protein S, FVa was incubated with APC (± protein S) in a purified prothrombinase assay.
Results: At the concentrations of lipids tested in our study, PS did not significantly impact clot structure or fibrinolysis. Similarly, eoxPL did not impact either fibrinolysis or activity of APC/Protein S.
Conclusion: Using liposome compositions that approximate activated blood cells, we found that the pro-coagulant membrane is unlikely to influence either clot structure or fibrinolytic activity directly, beyond its well characterized role in supporting Gla dependent coagulation factors and the actions of platelet associated proteins/receptors.
Keywords: activated protein C; fibrin; phosphatidylserine; phospholipids; plasmin; protein S.
© 2025 Morgan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
P.C. receives research funding from CSL Behring, Haemonetics Corp, Werfen, and consultancy from CSL Behring. Dr Josefin Ahnström was a consultant for Silence Therapeutics, grants from AstraZeneca Ltd, outside the submitted work. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Antonova O, Yakushkin V, Mazurov A. Coagulation activity of membrane microparticles. Biochem Moscow Suppl Ser A. 2019;13:169–186. doi: 10.1134/S1990747819030036 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

