Laterally π-Extended Polyhelicenes
- PMID: 41237299
- PMCID: PMC12673593
- DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c15494
Laterally π-Extended Polyhelicenes
Abstract
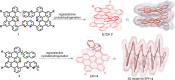
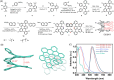
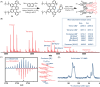
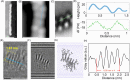
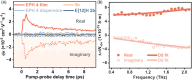
Helically coiled, semiconducting graphenic nanostructures show exceptional promise for nanoelectronics, yet their synthesis has remained challenging due to their inherently strained backbone and the difficulties associated with structural characterization. In this work, we demonstrate the synthesis and characterization of laterally π-extended polyhelicenes (EPHs), achieved through regioselective cyclodehydrogenation. Spectroscopic and microscopic analyses, including mass spectrometry, solid-state NMR, scanning-probe microscopy, and transmission electron microscopy, confirm the well-defined helical, layered architecture of the EPHs. Ultrafast terahertz spectroscopy reveals pronounced intrahelix photoconductivity, demonstrating their potential as carbon-based nanoscale conductors. The scalable synthetic approach described in this work unlocks the application potential of carbon-based helical nanostructures, paving the way for nanoinductors in nanoscale solenoids, spin-selective electronics, and future high-frequency nanoelectronic devices.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

