Case Report: Severe lead poisoning due to exposure to ayurvedic herbal medicine
- PMID: 41244251
- PMCID: PMC12611801
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2025.1692561
Case Report: Severe lead poisoning due to exposure to ayurvedic herbal medicine
Abstract
Introduction: Lead is an environmental toxin that may cause severe damage to vital organs including the brain, kidneys, liver, and bones. Children are particularly susceptible due to higher rates of gastrointestinal absorption and detrimental effects of lead on their developing nervous systems.
Methods: This report highlights the case of a 4-year-old boy with severe lead poisoning resulting from prolonged exposure to ayurvedic herbal supplements.
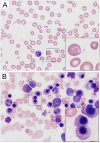
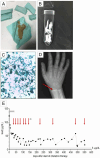
Results: The child was initially admitted with anemia, arterial hypertension, abdominal pain, and mild neurological impairment. His blood smear revealed pronounced basophilic stippling of erythrocytes. His venous blood lead level (BLL) was markedly elevated at 123 μg/dl. Detailed review of his history uncovered that he had been ingesting an ayurvedic herbal medicine for asthma. He received chelation therapy with 2,3-dimercapto-1-propanesulfonic acid and calcium disodium EDTA, resulting in rapid resolution of symptoms and gradually decreasing BLLs.
Conclusions: The case is a striking example of the significant health risks due to heavy metal contamination in ayurveda products. Better strategies to control the composition of ayurvedic products and educate families about their possible heavy metal contamination are essential to reduce the risk of lead poisoning.
Keywords: ayurvedic medicine; chelation therapy; complementary and alternative medicine; heavy metal toxicity; lead poisoning; pediatric environmental health.
© 2025 Cericola, Puzik, Salou, Yoshimi-Nöllke, Niemeyer, Feuchtinger, Henretig, Yip, Krell and Hettmer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- MN Dept. of Health. Metal toxicity from ayurvedic medications—MN Dept. of Health. Verfügbar unter: https://www.health.state.mn.us/communities/environment/lead/fs/ayurvedic... (Zugegriffen September 30, 2025).
-
- Choi Y, Polo F, Sripada K, Stewart L, Wickham A, Xu F, et al. The toxic truth: children’s exposure to lead pollution undermines a generation of future potential, UNICEF.
-
- World Health Organization. Lead poisoning. Verfügbar unter: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/lead-poisoning-and-health (Zugegriffen August 9, 2024).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

