From variant of unknown significance to actionable diagnosis: Stepwise interpretation of a novel KRT2 variant in superficial epidermolytic ichthyosis with excellent retinoid response
- PMID: 41244859
- PMCID: PMC12615286
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jdin.2025.09.006
From variant of unknown significance to actionable diagnosis: Stepwise interpretation of a novel KRT2 variant in superficial epidermolytic ichthyosis with excellent retinoid response
Keywords: dermatopathology; epidermolysis bullosa; genetic counseling; genetics/genodermatoses; immunobullous; keratin; machine learning; retinoids.
Conflict of interest statement
None disclosed.
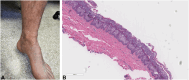
Figures
References
-
- Gameiro A., Cabral R., Moreno A., Tellechea O. Superficial epidermolytic ichthyosis-hypertrichosis as a clue to diagnosis. Pediatr Dermatol. 2016;33(6):e346–e348. - PubMed
-
- Walsh N., Cooper A., Dockery A., O'Byrne J.J. Variant reclassification and clinical implications. J Med Genet. 2024;61:207–211. - PubMed
-
- Kang H.Y., Park E.S., Nam S.M. Simultaneous combination treatment using high-intensity focused ultrasound and fractional carbon dioxide laser resurfacing for facial rejuvenation. Med Lasers. 2019;8(1):13–18.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

