A large language model-based approach to quantifying the effects of social determinants in liver transplant decisions
- PMID: 41249463
- PMCID: PMC12623799
- DOI: 10.1038/s41746-025-02025-y
A large language model-based approach to quantifying the effects of social determinants in liver transplant decisions
Abstract
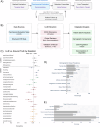
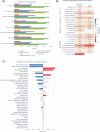
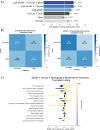
Psychosocial risk factors and social determinants of health (SDOH) contribute to persistent disparities in liver transplantation access. We developed a large language model framework to extract and analyze how these factors influence care trajectories. Prevalence of key modifiable barriers varied by demographics: social support gaps (35.4%, disproportionately affecting females), recent substance use (14.2-22.7%), and mental health challenges (17.6%, with Hispanic/Latino treatment gaps). Each factor was associated with 5-14 percentage point reductions in listing probability, comparable to clinical metrics. Psychosocial risk and SDOH factors explained 42.6% of racial disparities in listing decisions for Asian patients, exceeding liver health metrics (36.8%) and contributing to 94.6% collective explanation of differences. Priority interventions should target caregiver support, substance use, mental health, and patient education. This framework for systematically analyzing patient circumstances could enhance understanding of care decisions and health disparities.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: J.G. previously received research support from Merck and Co. He previously served on an advisory board for Gilead Sciences and previously consulted for Madrigal Pharmaceuticals and Astellas Pharmaceuticals/Iota Biosciences. J.C.L. receives research support from Lipocene and Vir Biotechnologies; receives an education grant from Nestle Nutrition Sciences; serves on an advisory board for Novo Nordisk; and consults for Genfit, Third Rock Ventures, and Boehringer Ingelheim. I.Y.C. receives research support from Alphabet/Google and Apple.
Figures



References
-
- Marmot, M. & Wilkinson, R. Social Determinants of Health (OUP, 2005).
-
- Marmot, M., Allen, J., Bell, R., Bloomer, E. & Goldblatt, P. WHO European review of social determinants of health and the health divide. Lancet380, 1011–1029 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Heidari, E., Zalmai, R., Richards, K., Sakthisivabalan, L. & Brown, C. Z-code documentation to identify social determinants of health among Medicaid beneficiaries. Res. Soc. Adm. Pharm.19, 180–183 (2023). - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

