Isolation, Identification and Typing of Nine Strains of Brucella in Arun Banner
- PMID: 41251272
- PMCID: PMC12624484
- DOI: 10.1002/vms3.70694
Isolation, Identification and Typing of Nine Strains of Brucella in Arun Banner
Abstract
Objective: To better understand the molecular biological characteristics and strain types of Brucella in Hulunbuir, Arun Banner, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, through isolation, biochemical identification, AMOS-PCR, and multiple locus sequence typing (MLST) of Brucella strains from human brucellosis patients, and to provide a reference for the scientific prevention and control of brucellosis in this region.
Method: The clinical and epidemiological data of patients with human brucellosis in Arun Banner, Inner Mongolia, were collected and analysed. Aseptically collected samples included venous blood, midstream urine and fresh diseased tissues (cerebrospinal fluid, synovial fluid, bone marrow, lymph node aspirates and abscess puncture fluids). Gram staining, serum agglutination, dye inhibition and phage lysis tests were used for the identification of Brucella species and biovars. Molecular identification and typing of Brucella were performed using AMOS polymerase chain reaction and multiple locus sequence typing (MLST).
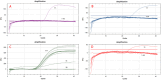
Results: Nine Brucella strains were isolated, all being B. melitensis: 2 biovar 1, 4 biovar 2, 2 biovar 3, and 1 variant. All infected individuals (9/9) were herdspersons, with a male-to-female ratio of 7:2 and an onset age of 30-63 years (mean 44). Among the cases, 88.89% became ill following contact with sheep, 66.67% were engaged in breeding work and 33.33% had direct contact with cattle and sheep. In MLST typing, seven strains were sequence type (ST) 8, one was a newly identified allele and one was ST12. Phylogenetic analysis using the neighbour-joining method showed that all nine isolates clustered with B. melitensis reference strains (M5, M28, 16 M, Rev.1), consistent with biochemical and PCR identification results.
Conclusion: People involved in raising and trafficking sheep constitute a high-risk group for brucellosis. The strains isolated were B. melitensis, with ST8 as the predominant type identified by MLST typing. Attention should also be given to the discovery of new alleles.
Keywords: biochemical identification; brucellosis; epidemiological investigation; multiple locus sequence typing.
© 2025 The Author(s). Veterinary Medicine and Science published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- 2018. “Prevention and Control of Brucellosis in Inner Mongolia.” Veterinary Journal 303, no. 17: 14–15.
-
- Corbel, M. J. 2006. Brucellosis in Humans and Animals. WHO Press.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

