Proof of concept for the usability of the IRRAMICE for proton preclinical radiobiological research by a traceable dosimetry evaluation
- PMID: 41257905
- PMCID: PMC12630642
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-24546-y
Proof of concept for the usability of the IRRAMICE for proton preclinical radiobiological research by a traceable dosimetry evaluation
Abstract
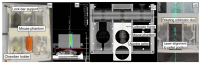
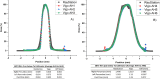
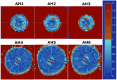
Radiobiology relies on animal studies to demonstrate efficacy and safety of treatments. For proton-based studies in clinical settings, bespoke solutions, enabling animal irradiations without compromising health and safety regulations, need to be developed to facilitate the research. This study aims to demonstrate the usability of the IRRAMICE, a novel system with bespoke collimators to effectively treat small targets, within proton clinical facilities. Following a clinical workflow of planning CT, treatment plan design and delivery, a dosimetric evaluation of the IRRAMICE was conducted. Traceable absorbed dose was determined by measurements with (i) ion chamber, (ii) alanine pellets within a mouse phantom and a bespoke holder in the IRRAMICE, and (iii) Gafchromic film in the holder for a relative evaluation of the collimation system. Dose determined with alanine pellets in the mouse phantom were within 2% of the planned dose. The 2%/2 mm local gamma analysis of the dose distribution of the collimated beam spot determined by the film and the treatment planning system showed an average 98.3% passing rate. Through measurements in mouse phantoms, IRRAMICE demonstrated to be a suitable device for enabling the setup and delivery of treatment plans in a reliable and reproducible manner, to facilitate in vivo preclinical experiments.
Keywords: Dosimetry; IRRAMICE; Preclinical; Proton therapy.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- PTCOG - Home. https://ptcog.site/
-
- Verhaegen, F. et al. Roadmap for precision preclinical x-ray radiation studies. Phys. Med. Biol.68, 06RM01 (2023). - PubMed
-
- Paganetti, H. et al. Relative biological effectiveness (RBE) values for proton beam therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys.53, 407–421 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Dosanjh, M., Jones, B., Pawelke, J., Pruschy, M. & Sørensen, B. S. Overview of research and therapy facilities for Radiobiological experimental work in particle therapy. Report from the European particle therapy network radiobiology group. Radiother. Oncol.128, 14–18 (2018). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

