Subwavelength grating-assisted silicon nitride edge coupler with relaxed alignment tolerance
- PMID: 41258432
- PMCID: PMC12630908
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-26434-x
Subwavelength grating-assisted silicon nitride edge coupler with relaxed alignment tolerance
Abstract
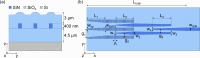
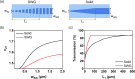
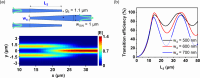
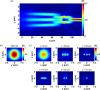
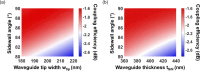
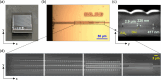
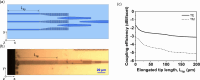
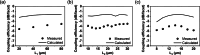
We propose and realize a silicon nitride (SiN) edge coupler with enhanced alignment tolerance, achieved through the integration of a subwavelength grating (SWG) structure. The incident optical mode is guided from the SWG tri-tip to the main waveguide via two adiabatic transitions through intermediate bridge waveguides. The SWG tri-tip, composed of three laterally arranged SWG waveguides, provides a broader horizontal optical input region than a single-tip design, enhancing horizontal alignment tolerance. Moreover, careful engineering of the SWG period and fill factor lowers the effective index of the input waveguide compared to a solid waveguide, improving mode matching with optical fibers. The fabricated device demonstrates 1-dB alignment tolerances of ± 3 μm in the horizontal direction when coupled with a standard SMF-28 optical fiber, achieving a measured coupling efficiency of - 3.8 dB/facet at 1550 nm wavelength. This horizontal tolerance is notably wider than that of conventional single-tip inverse-tapered edge couplers, validating the effectiveness of the SWG tri-tip design in expanding the input acceptance region. These results highlight the effectiveness of the proposed design in relaxing alignment sensitivity while maintaining efficient coupling, making it suitable for practical packaging and integration in SiN photonic platforms.
Keywords: Alignment tolerance; Edge coupler; Silicon nitride; Subwavelength grating.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- Kachris, C. & Tomkos, I. A survey on optical interconnects for data centers. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor.14(4), 1021–1036 (2012).
-
- Taubenblatt, M. A. Optical interconnects for high-performance computing. J. Lightwave Technol.30(4), 448–458 (2012).
-
- Biberman, A. & Bergman, K. Optical interconnection networks for high-performance computing systems. Rep. Prog. Phys.75, 046402 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Rumley, S. et al. Optical interconnects for extreme scale computing systems. Parallel Comput.64, 65–80 (2017).
-
- Young, I. A. et al. Optical technology for energy efficient I/O in high performance computing. IEEE Commun. Mag.48(10), 184–191 (2010).
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

