Sustainable green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles utilizing Zingiber officinale peel aqueous extract, characterization, and determination of its anticancer and antimicrobial potential
- PMID: 41259302
- PMCID: PMC12629472
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0334685
Sustainable green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles utilizing Zingiber officinale peel aqueous extract, characterization, and determination of its anticancer and antimicrobial potential
Abstract
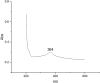
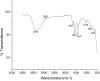
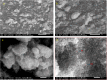
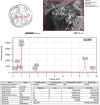
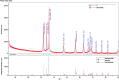
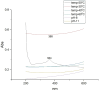
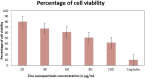
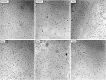
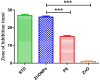
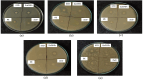
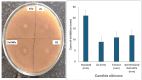
This study demonstrates the green synthesis, characterization, and biomedical applications of zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnONPs) using Zingiber officinale (Z. officinale) (ginger) peel extract. Green synthesis offers advantages over conventional methods, including environmental friendliness, cost-effectiveness, and enhanced biocompatibility. Ultraviolet-Visible (UV-Vis) spectroscopy confirmed ZnONPs formation with a peak at 364 nm. Fourier-Transform Infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy analysis revealed characteristic peaks indicating functional groups involved in nanoparticle formation. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) analysis showed spherical/agglomerated nanoparticles, and Energy-Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (EDS) confirmed 77.7% zinc oxide by mass%. The X-ray Diffraction (XRD) indicated an average particle size of 24.67 nm with distinct crystal orientations. Phytochemical analysis detected alkaloids, saponins, and steroids in the extract. Optimal synthesis occurred at 50-60°C and pH 10, yielding stable ZnONPs. The ZnONPs exhibited significant antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus), Bacillus subtilis (B. subtilis), Bacillus cereus (B. cereus), Escherichia coli (E.coli), Zymomonas mobilis (Z. mobilis), and Pseudomonas aeruginosa (P. aeruginosa), as well as antifungal activity against Candida albicans (C. albicans). The in vitro cytotoxicity study on M.D. Anderson - Metastatic Breast - 231 (MDA-MB-231) breast cancer cells showed a dose-dependent reduction in cell viability [Half-maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) = 82.13 µg/mL] with notable morphological changes at higher concentrations. The ZnONPs synthesized from ginger peel extract are innovative, environmentally friendly, and economical. Our findings show that biologically generated ZnONPs are effective antibacterial and antifungal agents against several pathogens. This research uniquely demonstrates the potential of ginger peel, a commonly discarded agro-waste, as a sustainable source for ZnONPs synthesis, highlighting its biotechnological and medicinal applications. The novelty of this study lies in the green synthesis approach using ginger peel and the comprehensive evaluation of its antimicrobial and anticancer properties. Further in-depth studies and optimization are needed to validate their therapeutic efficacy and safety.
Copyright: © 2025 Alqahtani et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Chikkanna MM, Neelagund SE, Rajashekarappa KK. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnONPs) and their biological activity. SN Appl Sci. 2019;1:1–10.
-
- Aldeen TS, Ahmed Mohamed HE, Maaza M. ZnO nanoparticles prepared via a green synthesis approach: physical properties, photocatalytic and antibacterial activity. J Phy Chem Solids. 2022;160:110313. doi: 10.1016/j.jpcs.2021.110313 - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

