Additive Benefits of Control-IQ+ AID to GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Use in Adults With Type 2 Diabetes
- PMID: 41264828
- PMCID: PMC12635876
- DOI: 10.2337/dc25-1753
Additive Benefits of Control-IQ+ AID to GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Use in Adults With Type 2 Diabetes
Abstract
Objective: To assess the effect of automated insulin delivery (AID) on glycemic and insulin outcomes in adults with insulin-treated type 2 diabetes using a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1 RA).
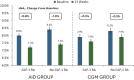
Research design and methods: In a randomized trial comparing Control-IQ+ AID versus continuation of prestudy insulin delivery method plus continuous glucose monitoring (CGM group), 143 (45%) of the 319 participants were using a GLP-1 RA at baseline, which was continued during the trial.
Results: Among GLP-1 RA users, mean HbA1c decreased by 0.8% from a baseline of 8.0 ± 1.2% with AID, which represented a mean improvement of -0.5% (95% CI -0.8 to -0.3, P < 0.001) compared with the CGM group. Time-in-range 70-180 mg/dL and other CGM metrics reflective of hyperglycemia also showed comparable statistically significant improvements using AID when added to GLP-1 RA use. For GLP-1 RA users, there was no significant difference in weight after 13 weeks with AID compared with the CGM group (0.9 kg, 95% CI -0.2 to 2.1, P = 0.10), whereas, in GLP-1 RA nonusers, there was a mean weight gain of 1.9 kg with AID compared with CGM (95% CI 0.5 to 3.2, P = 0.007).
Conclusions: The benefits of AID appear to be substantial for a broad spectrum of insulin-treated patients with type 2 diabetes, including those already receiving contemporary and guideline-directed therapy, such as a GLP-1 RA medication. These additive benefits of AID in GLP-1 RA users included significant reductions in HbA1c levels with simultaneous reduction in insulin use, along with no statistical increase in weight despite very significant improvements in glycemic control.
© 2025 by the American Diabetes Association.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Kudva YC, Raghinaru D, Lum JW, et al.; 2IQP Study Group . A randomized trial of automated insulin delivery in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2025;392:1801–1812 - PubMed
-
- Perkovic V, Tuttle KR, Rossing P, et al.; FLOW Trial Committees and Investigators . Effects of semaglutide on chronic kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2024;391:109–121 - PubMed
-
- Packer M, Zile MR, Kramer CM, et al.; SUMMIT Trial Study Group . Tirzepatide for heart failure with preserved ejection fraction and obesity. N Engl J Med 2025;392:427–437 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical